TechnologySeptember 22, 2019
Next-generation IIoT gateways transform smart manufacturing
Manufacturing companies have a great opportunity to benefit from the IIoT trend, powered by the benefits of new IIoT gateways. Intelligent edge-computing solutions are providing a mechanism to bridge the worlds of OT and IT, and offer new ways to increase productivity, reduce downtime and increase product quality.
Smart manufacturing and digital transformation, coupled with edge intelligence, are enabling manufacturers to increase productivity, reduce downtime, and increase product quality. A key factor in the success of this transformation is the deployment of intelligent edge-computing solutions that can bridge the gap between the operation technology (OT) and the information technology (IT) worlds by providing a number of benefits. In this article, we discuss what manufacturers need to benefit from the IIoT trend and how a new generation of IIoT Gateways are helping them reap the benefits of the IIoT, thereby transforming their businesses.
Reduced latency
Manufacturers are expected to be more responsive to customer needs by providing customized products and services on a global scale. In addition, time-sensitive applications need immediate processing of device data to be able to take timely corrective actions and facilitate quick decision-making. Edge intelligence can facilitate quick decision-making at the field sites as opposed to sending all the device data from the edge to the cloud for processing.
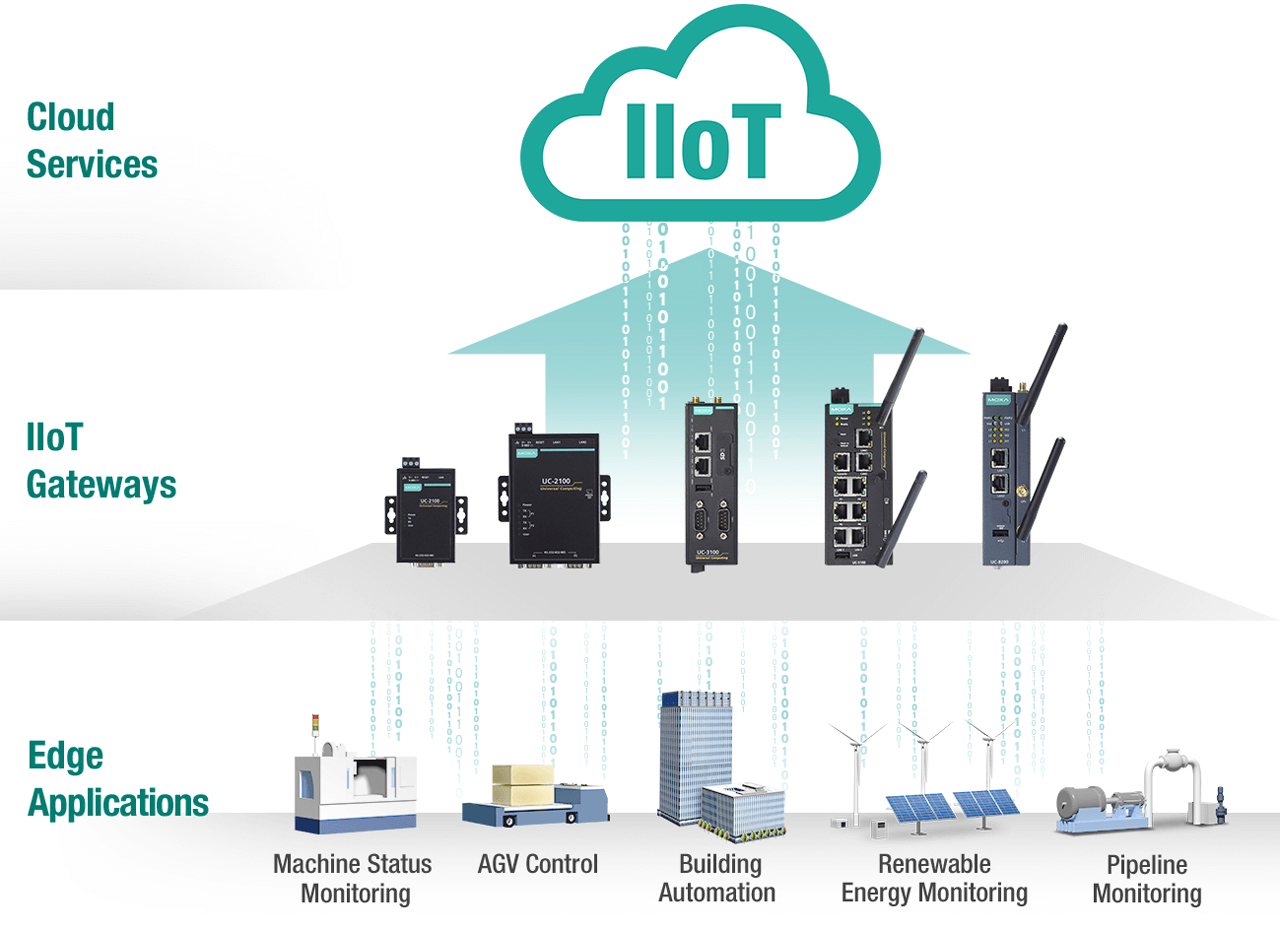
Key benefits of IIoT gateways combine industrial-grade Linux, low power consumption and secure operation into solutions that support multiple interfaces/protocols and provide easy connectivity from the edge to the cloud.
Independent remote operations
An edge-computing platform enables remote locations to reduce downtime and operate independently when the central system is inaccessible. For example, if there is a network outage and connectivity to the cloud system is lost, field sites can use local computing power to process and analyze data. Processed data can then be sent to the cloud for long-term storage when the connection is restored.
Data security
Sending sensitive operational data from the edge to the cloud puts data and edge devices at risk. Multiple levels of security need to be put in place to ensure that the data is securely transferred from the edge device to the cloud. Processing data at the edge helps prevent data breaches and enables faster responses.
Reduced data-transfer costs
Transferring large volumes of data from the edge of the network to a cloud server can be prohibitively expensive. Furthermore, the cost of transferring this data on a daily basis could lead to unsustainable communication costs in the long run.
Manufacturers are looking for optimized computing solutions for their industrial-automation applications to intelligently process large volumes of data received from the sensors and field monitors, and send only critical data or a summary of the data to the cloud. Compact-sized, ruggedized industrial Arm-based computers, designed for low power consumption, are at the heart of these solutions and make edge-side computing more reliable and cost-effective.
Benefits of Arm-based Linux
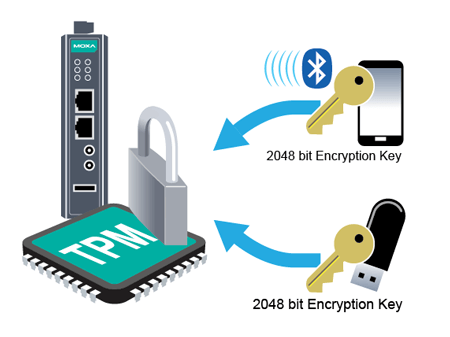
TPM and Arm-based computers give system integrators and engineers powerful new tools in their security arsenal.
Arm-based Linux IIoT Gateway solutions provide industrial-grade security, manageability, performance, and reliability while still maintaining extensibility. They typically combine the hardware, OS, and software functions listed below to provide an optimized edge-computing solution for IIoT applications.
Longevity: Industrial products are usually in place for 10 to 15 years. To meet this requirement, Arm-based CPUs typically come with a minimum lifespan of 15 years. In addition, Arm’s commitment to long-term support and access to their future enhancements, make Arm- based solutions an ideal choice for industrial applications.
Low Power Consumption: Low-power processing is a requirement in many industries to ensure that the equipment does not overheat and pose a potential hazard. Fanless equipment are also preferred so as to mitigate the effects of dust in industrial environments. Arm Cortex-A processors are highly optimized for performance and power efficiency.
Scalability: Linux is eminently scalable and is able to run on a variety of platforms. The basic functionality of a Linux platform—command line tools, configuration, and code—are compatible with any Linux-based device. This flexibility allows for easier upgrades and compatibility between different systems.
Enhanced Security: While manufacturers are reaping the benefits of digitization, they are also faced with data security risks and software-integrity issues. A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) can be deployed to guarantee the physical security of edge devices. In addition, Arm’s TrustZone can be used to create an isolated secure world, which can enhance security and maintain the integrity of edge-computing solutions.
Ready-to-run IIoT gateways
A new generation of IIoT Gateways that are optimized for industrial applications are revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape. Built around an open Linux-based platform, these IIoT gateways are secure, industrial-grade computing platforms that support multiple communication interfaces and run on low power.
Industrial-grade Linux
IIoT gateway solutions that include a high-performance industrial-grade Linux distribution and long-term support are better equipped to meet the growing needs of manufacturers. Currently, long-term support (LTS) offered on a Linux kernel is five years. In most industrial establishments, especially in critical systems such as energy, water, transportation, and communication, it is not feasible to update the software systems every 5 years. Software vendors should commit to long-term maintenance of the Linux platform. A long-term commitment (10 years or more) to support a Linux kernel, which includes security patches and bug fixes will address the needs for extended lifecycle of computing systems in industrial automation applications, making industrial projects secure and sustainable.
Projects, such as the Civil Infrastructure Platform (CIP), aim to speed implementation of Linux-based civil infrastructure systems, build upon existing open source foundations and expertise, establish de facto standards by providing a base layer reference implementation, and contribute to and influence upstream projects regarding industrial needs. CIP’s kernel will be based on Linux kernel 4.4 and will include security patches and features backported from newer kernels.
CIP is driven by some of the world’s leading manufacturers of civil infrastructure systems and industry leaders including Codethink, Hitachi, Plat’Home, Renesas, Siemens, Moxa, and Toshiba. This project is hosted by The Linux Foundation to create an open-source platform for managing and monitoring IoT-enabled civil infrastructure and make it safe, secure, reliable, scalable, and sustainable.
Other related projects include the Core Infrastructure Initiative (CII) and the Kernel Self Protection Project.
A reliable and secure solution ensures that needed data is brought back to the control center for further analysis.
Low power consumption
It is a well-known fact that when it comes to low-power systems, Arm-based systems are a natural choice. Intel based x86 IIoT gateways consume on an average 30 W of power while their Arm-based counterparts, for example, gateways build on the Arm Cortex-A processor, can provide industrial-grade performance in power budgets under 10 W. Low power computers and devices help substantially reduce your operational costs. They consume less power and hence generate less heat, which means no cooling systems are required.
Secure platform
Operational networks were simply not built for connectivity to the Internet/cloud. The key focus of these networks is quick data access for industrial processes. Manufacturers feel that implementing multiple security levels is a huge drain on network resources and may impact productivity. However, in the IIoT age, where the trend is towards more connectivity for edge device, which may otherwise never be connected to the Internet, there is a quantum increase in possible attack points for malicious attackers.
Security threats can extend to even low-level devices. Cyber attackers can target anything that is exposed to the Internet, including a thermostat in the field to a wireless device. Manufacturers can longer take this threat lightly. Information security, system hardening, security fixes, and ability to backport fixes to existing cores without having to change the software helps organizations better fight cyberattacks.
One example is Arm-based computers that support TPM v2.0. Bringing TPM and Arm-based computers together gives system integrators and industrial engineers a powerful new tool in their security arsenal. By creating a specific cryptographic key for each individual device, which is hardcoded within the platform itself, the data stored on the computing system is secured and protected from being read by an unauthorized party. Moreover, the OS on the system can be locked from being overwritten to secure edge devices and data in distributed areas. Security utilities and tools that can conveniently build up the protection mechanism on the software platform to meet your cybersecurity requirements are other ways to secure industrial systems.
Multiple interfaces and protocols
IIoT Edge Gateways should come with multiple interfaces such as serial, CAN, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and NB-IoT. 4G LTE-ready. IIoT gateways with carrier (Verizon/AT&T) certifications and industrial-grade CE/FCC/UL certifications enable reliable connectivity for edge devices.
An edge-side software that accelerates mass configuration of devices, easy device management, and data acquisition can speed up system deployment. Modbus connectivity for data acquisition and processing and MQTT support for lightweight edge-to-core data transmission reduce development efforts. RESTful APIs and Modbus APIs for implementing gateway software functions enable easy integration with existing systems and with new-age IIoT applications.
Easy connectivity to the cloud
Edge intelligence and connectivity to the cloud are two faces of the same coin. Depending on the IIoT applications, connectivity to a private cloud, public cloud, or both may be required. To enable cloud connectivity and edge intelligence, generic Modbus and EtherNet/IP protocol support, MQTT /HTTPS and RESTful/ C/Python API support are required. Built-in clients for AWS, Azure, Ignition Edge (Sparkplug), and Wonderware Online services may also be necessary, depending on the cloud services that are required for your IIoT applications.
The following two cases illustrate how new-age IIoT gateways help speed up IIoT deployments and transform operations based on intelligence from field data.
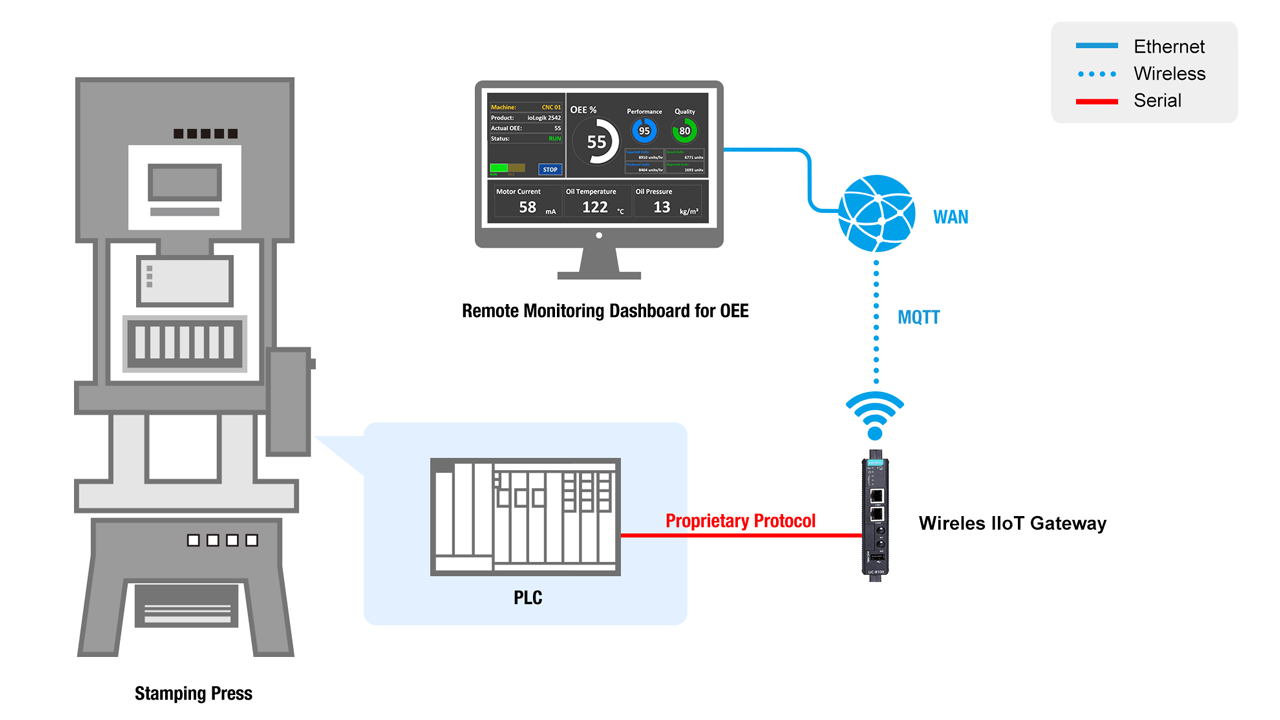
Machine Data Acquisition (PLCs)
Traditional machine tool builders are now willing to invest in new IIoT trends so that they can provide more value with their products and improve the quality of machine status data collected for post-sales management and services.
The data acquisition system must be capable of acquiring data from different brands of PLCs with their own proprietary protocols, send the data to backstage control server, and display the data on a dashboard remotely and locally. Furthermore, a compact and reliable device for data acquisition is required without having to changing the structure of machines which means the system should be small enough to fit in existing control cabinets.
System Requirements
- Computing solution to collect data from PLC to monitor the status of the stamping press remotely and locally through Wi-Fi
- The solution should work with a variety of Mitsubishi, Delta, and Allen-Bradley PLCs
- Compact-sized and vibration-proofed systems for reliable operation in the cabinet of the stamping press
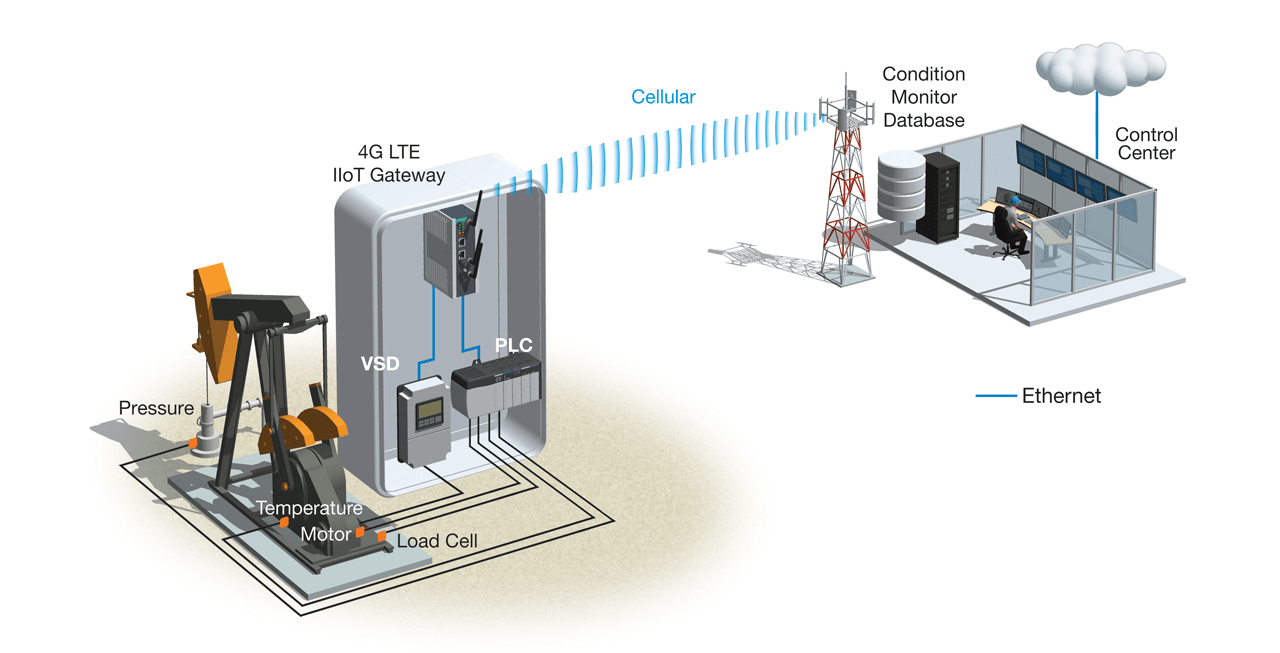
Artificial lift monitoring systems
A leading oil and gas service company is building telematics solutions for its customers to run smooth operations and conduct predictive maintenance for artificial lifts in oilfields. With the trend of oilfield digitization, telematics has been tremendously useful in understanding equipment status so as to avoid problems, also called predictive maintenance.
The data generated by the manufacturing equipment during the operations is the key to achieving this goal. As a result, this oil and gas service company needs a reliable and secure solution to ensure that the data needed is brought back to the control center for further analysis.
A wireless-enabled Arm-based open computing platform that acts as a secure IIoT gateway, allows oil companies to aggregate data from variable speed drives (VSDs) and PLCs for their pumping systems and to transfer the data back to the control center through LTE communication in the harshest environments.
A built-in Trusted Platform Module (TPM) in the IIoT gateway can ensure that each individual device is hardcoded by a cryptographic key to ensure the data is only accessible by authenticated parties.
System Requirements
- Low power consumption because oil wellheads are often located in harsh environments where powering is sometimes difficult
- Reliable 4G LTE connectivity in high operating temperatures for constant data aggregation
- Computers must feature Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to ensure data integrity
- Open Linux platform for flexible application development
Wireless IIoT gateway solutions
UC series IIoT edge gateway technology offers industrial-grade, wireless-ready Arm-based computing platforms that are designed to operate reliably in a wide temperature range of -40 to 85°C. These gateways are built around the Arm Cortex-A processor and come with Moxa Industrial Linux (MIL) to address the need for extended lifecycles in computing systems for sectors such as solar/wind power, water and wastewater, oil and gas, transportation, and factory automation. Key benefits include:
- Industrial-grade Linux
- Low power consumption
- Secure platform
- Multiple interfaces and protocols
- Easy connectivity from edge to the cloud
The UC series IIoT Edge Gateways are the first Azure IoT Edge certified Arm-based computers. Integrating Azure IoT Edge with the gateways benefits customers, especially those operating on Linux platforms, in a number of ways. The benefits include secured remote connections to enable deployment in remote locations, connectivity to allow existing brownfield applications to share data with the cloud, and device management and product longevity to ensure customers can deploy, scale, and maintain their IIoT applications.

