TechnologyNovember 18, 2021
The journey to provisioning & maintenance with RACER
In today’s world where network manageability plays an increasingly critical role in a network’s ability to efficiently scale, having a platform is significantly vital. With the conveniences that RACER provides, it’s almost effortless to securely configure, document, and manage Cisco URWB devices on a network of any size.
Data Networks have always demanded a means of configuration manageability in one way or another, especially when so much emphasis is placed on its ability to scale while maintaining coherent device management.
In general terms, the more devices added to a Data Network, the more challenging and time-consuming it becomes for the Network Administrator to distribute, manage, and modify configurations for each of these devices on the network.
Device management tools have been around for decades and come in many forms – from terminal emulators utilizing the Secure Shell protocol to Graphical User Interface applications. These tools all had one goal in common – to efficiently distribute, apply, and modify device configurations on networks small to large in size.
RACER Network Management System
The Cisco Ultra Reliable Wireless Backhaul (Cisco URWB) RACER (Radio Configuration Environment) platform allows just that, by providing an intuitive, secure, and efficient platform which allows devices to be configured from a centralized cloud platform. This by no means removes the conventional step of creating a document for each project, which captures all the pertinent configuration details needed per device, and usually in the form of a spreadsheet.
With this documentation method, it is an efficient way to use these details for the creation of configuration mappings on the RACER platform online. The RACER platform uses Transport Layer Security (TLS), and can be accessed via the link https://partners.fluidmesh.com/.
With RACER, End-Users are able to easily identify radios categorized based on specific projects within their organization. Once a user profile is created on the portal, a database of Cisco URWB devices and licenses associated with the user profile or organization are accessible on the RACER cloud portal. With this centralized convenience, it’s now easy for users to:
- Apply and Remove plugin and support licenses to device profiles.
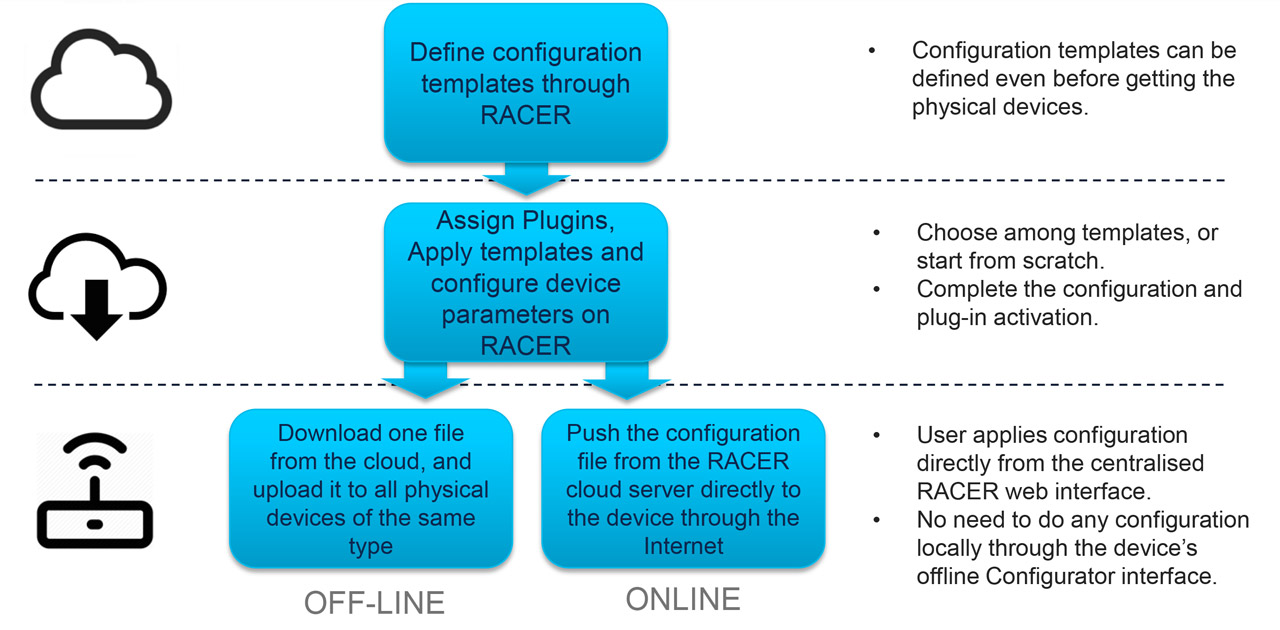
- Create and apply configuration templates for devices based on network roles.
- Directly sync cloud configuration settings to the Cisco URWB devices using the online configuration feature.
- A single configuration file can be downloaded from the RACER portal and uploaded to each device locally using the offline configuration feature, which in turn allows the respective radio to pull the requisite configuration.
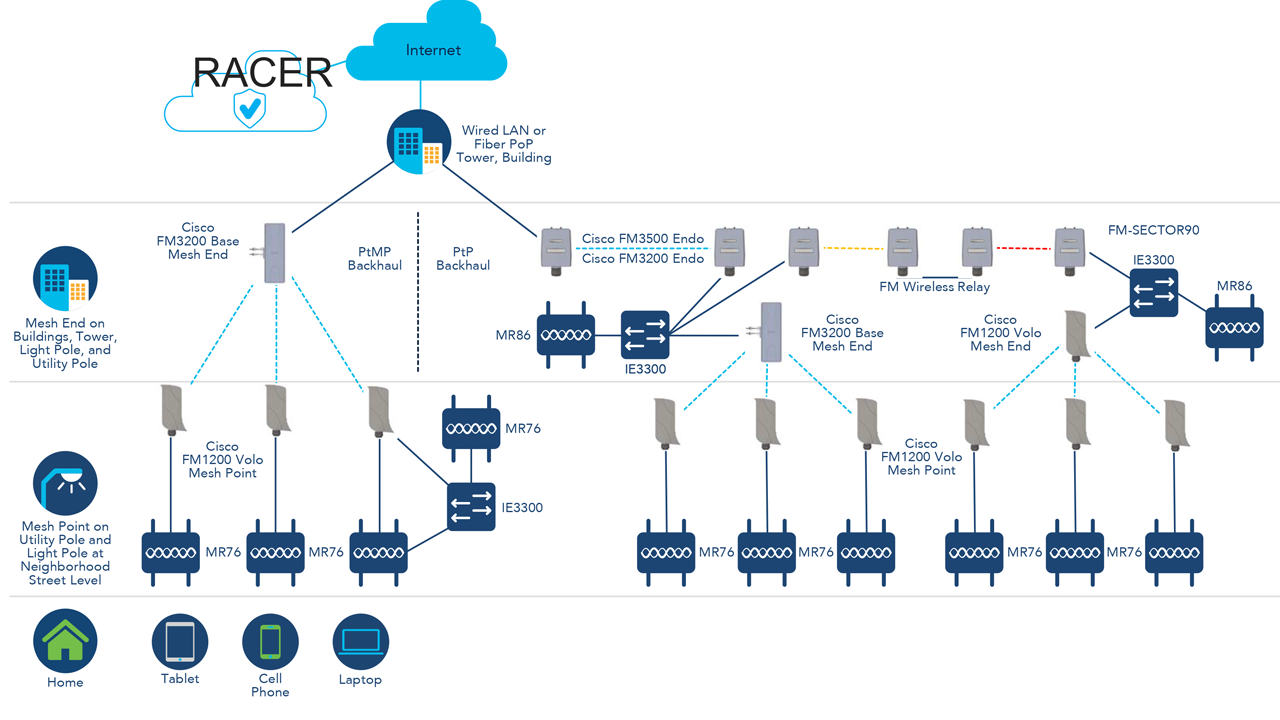
One of the key benefits of RACER is the plug and play ability. For new device implementations, Cisco URWB devices can be synchronized with the configurations defined on the RACER platform once they are plugged into a network source that has internet access and DHCP services. The devices are able to connect with the RACER platform and automatically download and apply configurations that have been mapped to the specific devices Mesh ID. The Mesh ID is a unique, four octet number that each Cisco URWB device has. Think of it being similar to a serial number.
With the ability to have configurations applied to devices in such a seamless manner, it is easy to manage medium to large network deployments. This is also very beneficial post deployment.
As seen in the image on page 53, for networks that are already deployed, once these devices have a connection to the internet through the core network, configuration changes relative to a device’s Mesh ID can be made on RACER and automatically pushed to devices in the field. The most recent firmware updates for these devices are also included in the configurations pulled down from RACER once new versions are available, which keeps devices consistent across the board.
The caveat to this is, radios have two modes of configuration depending on the method that is most convenient or practicable based on the network environment. For networks without a direct internet connection to the Cisco URWB devices, the device configuration mode can be set to offline configuration. With this mode selected, network administrators are able to download a single file from RACER that has all the configuration settings previously mapped.
A user can determine which devices they want to be part of the configuration file by selecting checkboxes that correspond to the respective device Mesh ID’s, or as an option all devices can be selected.
Once the file is downloaded, the file can be uploaded to each respective device. The devices will intuitively pull configurations and licensing information as necessary based on configuration mapping made to the Mesh ID’s on RACER.
In today’s world where network manageability plays an increasingly critical role in a network’s ability to efficiently scale, having a platform such as RACER is significantly vital. With the conveniences that RACER provides, it’s almost effortless to securely configure, document, and manage Cisco URWB devices on a network of any size.
Technology report by Cisco Systems


