TechnologyMarch 30, 2021
5G with TSN for industrial communications
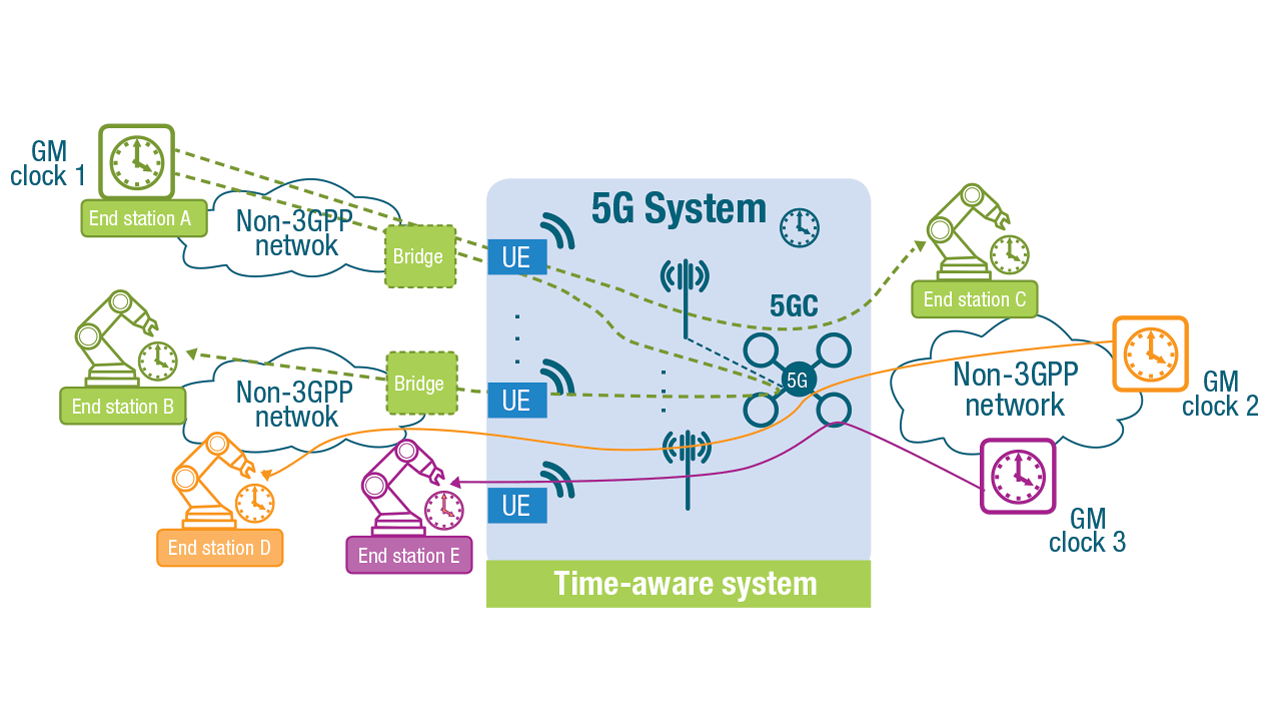
A prevailing view is that integration of 5G and TSN will increasingly become more important to industrial automation in the future. The thinking is that TSN, as enabling technology of Industry 4.0 together with 5G URLLC, can be combined to provide deterministic connectivity end-to-end.
The integration of 5g and TSN could be an important future step to make smart factories more fully connected, and able to meet all key requirements for more effective industrial communication technology.
Industrial automation is already in the midst of digital transformation, and a process of interconnecting multiple machines, devices, the cloud and people with a goal of making information accessible from anywhere within a factory.
5G has the potential to provide a highly effective wireless solution that could be used in combination with TSN especially in time-sensitive applications that require deterministic, reliable and low-latency communications.
5G ACIA
With a goal to make 5G a success for industrial applications, the trade group 5G-ACIA (ww.5g-acia.org) is bringing together organizations from the OT and OT worlds.
According to the “Integration of 5G with Time-Sensitive Networking for Industrial Communications” white paper published by 5G ACIA, 5G has been standardized with all the necessary support to seamlessly integrate with industrial TSN networks. But they also acknowledge that the future evolution of TSN will have to be matched by 5G enhancements in coming releases.
The executive summary of the paper states that “fifth-generation wireless communications (5G) and time-sensitive networking (TSN) technologies are key to future industrial communications: 5G for wireless connectivity and TSN for wired connectivity.”
“Both technologies have been designed to provide converged communication for a wide range of services on a common network infrastructure, including for time-sensitive applications that require deterministic, reliable and low-latency communications. Significant benefits can be achieved for corresponding industrial use cases by introducing TSN and 5G wireless communication, e.g., increased flexibility in the deployment of industrial equipment and the network.”
The 5G-ACIA white paper describes the main TSN features including TSN traffic scheduling (IEEE 802.1Qbv), per-stream filtering and policing (IEEE 802.1Qci), time synchronization (IEEE 802.1AS), frame replication and elimination for reliability (IEEE 802.1CB), and TSN network configuration (IEEE 802.1Qcc).
It also addresses the work-in-progress in IEC/IEEE 60802 on defining a TSN profile for industrial automation along with typical use cases for TSN in industrial automation, different traffic types and the corresponding communication requirements.
Avnu Alliance
The Avnu Alliance (www.avnu.org) has also published a white paper “Wireless TSN –Definitions, Use Cases & Standards Roadmap” that provides insights into the potential of 5G and TSN working together.
It concludes that “recent advances in 5G and IEEE 802.11 wireless connectivity technologies in providing low latency and high reliability have generated significant interest in extending TSN capabilities over wireless. Wireless communication systems are beneficial for many obvious reasons, including enabling flexibility and reducing wiring costs as well as enabling mobility.”
Because of the complexity of wireless communications, enabling TSN capabilities that are interoperable and compatible with existing wired TSN standards will be challenging but the potential benefits could make a major impact in industrial automation.