TechnologySeptember 20, 2021
Optimize power consumption using remote monitoring
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) generates a tremendous amount of data that also needs to be stored. Consequently, more and more data centers are needed to fulfill this growing demand for data storage management, increasing energy consumption in the process.
Data center operators and application owners need to operate numerous servers and power-hungry equipment while optimizing power consumption. Power distribution units (PDUs) are used to control and distribute power to various equipment. Nowadays, intelligent PDUs that feature metering and switching capabilities from remote sites have seen significant market growth due to increasing remote monitoring demands.
In fact, a recent report identifies the increasing demand for data center monitoring solutions as the key driver of PDU market growth. Monitoring PDUs in an application not only helps optimize energy usage, by recording daily power consumption for payment calculation and energy management, but also allows collection of data about the status of PDUs for device maintenance.
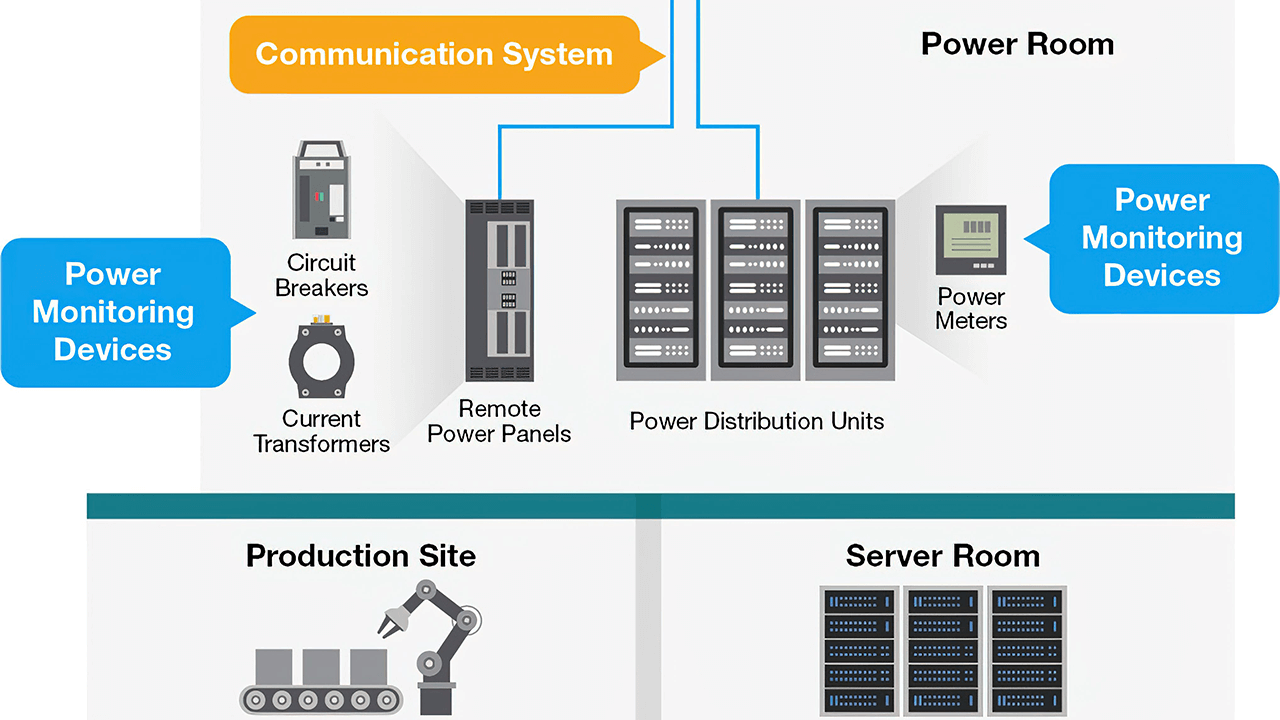
According to Moxa to reap the benefits of monitoring PDUs, an energy management system (EMS) needs to collect meter data from PDUs so that operators can control, monitor, and optimize the performance of the PDUs. In addition, remote power panels (RPPs) may also be used as an extension of PDUs to increase the power distribution capacity by providing extra circuits. Thus, it’s also important to monitor the circuit breakers and current transformers to ensure that power distribution through different circuits is under control.
It takes reliable connectivity between the EMS and power devices, such as PDUs and RPPs, to ensure smooth and optimized power distribution. Here are tips to consider to ensure reliable connectivity in between.
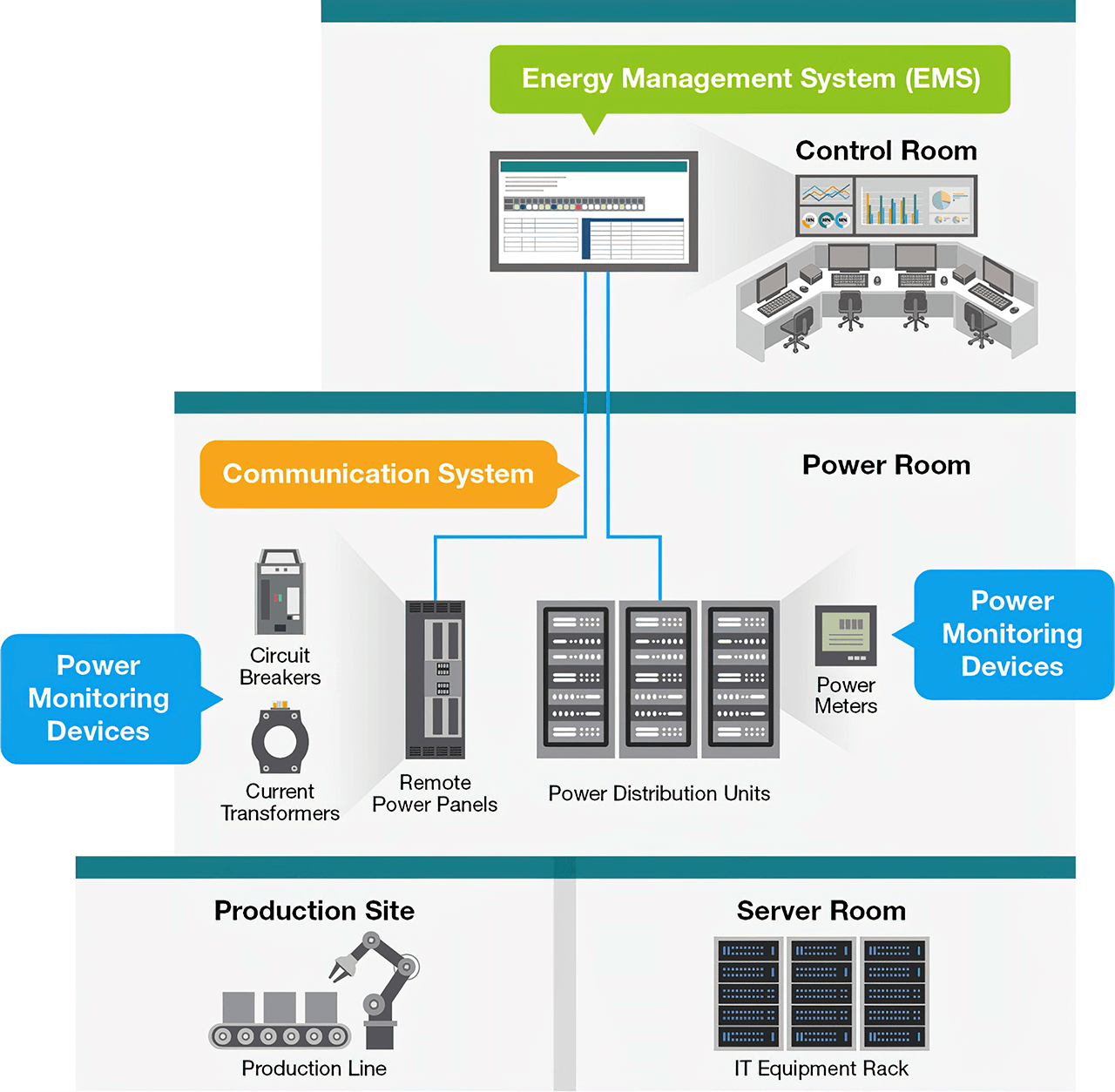
Typical system diagram.
Retrofitting or building new?
Once a user decides to monitor the PDUs and RPPs in an application environment, the question about enabling connectivity depends on the implementation plan. Besides connecting power meters, circuit breakers, and current transformers that might use different protocols and interfaces than your EMS, ask the following questions.
Is the goal to retrofit existing PDUs or deploy a new one? Is there enough space for wiring design? How many PDUs will be connected to the network?
Answers to the above questions will reveal the need for a single-port or high port-density connectivity solution. For example, if you have limited space for retrofitting your existing PDUs in a relatively small-scale application, a single-port connectivity solution may be the ideal option due its compact design. In contrast, high port-density connectivity solutions can help save on costs if there is sufficient space to deploy multiple new PDUs.
Choosing an easy-to-use connectivity solution can save significant time and effort. In the installation stage, wiring can be painful when you are connecting dozens of PDUs to the same network. Check if the selected connectivity solution has features such as Ethernet cascading, which provides an efficient wiring solution across several PDUs and RPPs to the EMS located in the control center. When PDUs and RPPs are up and running, networking devices will still require backups and updates from time to time.
When unexpected network failures occur, meter data loss can lead to miscalculation of power consumption data, resulting in incorrect billing and incomplete power data for analytics. To enhance power monitoring system reliability, consider backup mechanisms from different angles. Start from the networking devices.
Dual-power inputs and high EMI immunity are features that can protect networking devices from electrical interference. Next, develop a redundancy mechanism for network transmissions. There are various network redundancy features in the market. When considering these options, see if their recovery times are acceptable for the needs of the power monitoring application.
Application article by Moxa