TechnologyMay 30, 2021
5G isn’t for everyone: How Alternate IoT Solutions come into play
Complementary IoT solutions are filling the gap here where 5G may be costly, or when deployments simply cannot support its infrastructure. While options for IoT solutions are seemingly endless, it’s important to understand the needs of the deployment, and which solution can deliver.
While the hype around 5G has been quite significant, the reality is that it’s a long-term investment and users won’t experience the technology’s full capabilities for quite some time. To date, 5G deployments have been focused on applications requiring higher capacity, higher data rates and lower latency. But 5G isn’t a one size fits all solution, and while the demand for it continues, there’s a growing need for complementary IoT solutions where 5G won’t necessarily be most effective.
5G solutions require substantial infrastructure support, constant connectivity and immense bandwidth to support the large amount of data flowing from end-user solutions and devices. Many IoT solutions do not need that level of connectivity and in many cases, simply do not need the high end and high energy consumption hardware to support constant broadband connectivity.
With the demand for 5G comes a simultaneous need for complementary solutions that can fill this gap. We’re seeing this need grow even higher as we’re spending more time at home than ever before, and are relying on connectivity for education, work and employment opportunities, health care and far more.
5G may seem like the IoT network that you should deploy given its industry presence, however, every technology brings specific capabilities and benefits to each unique deployment. With that said, it’s important for municipalities, organizations and even individuals to understand what their needs are, and which technology can help cater to their demand.
In addition to 5G, here are a few IoT network technologies to consider:
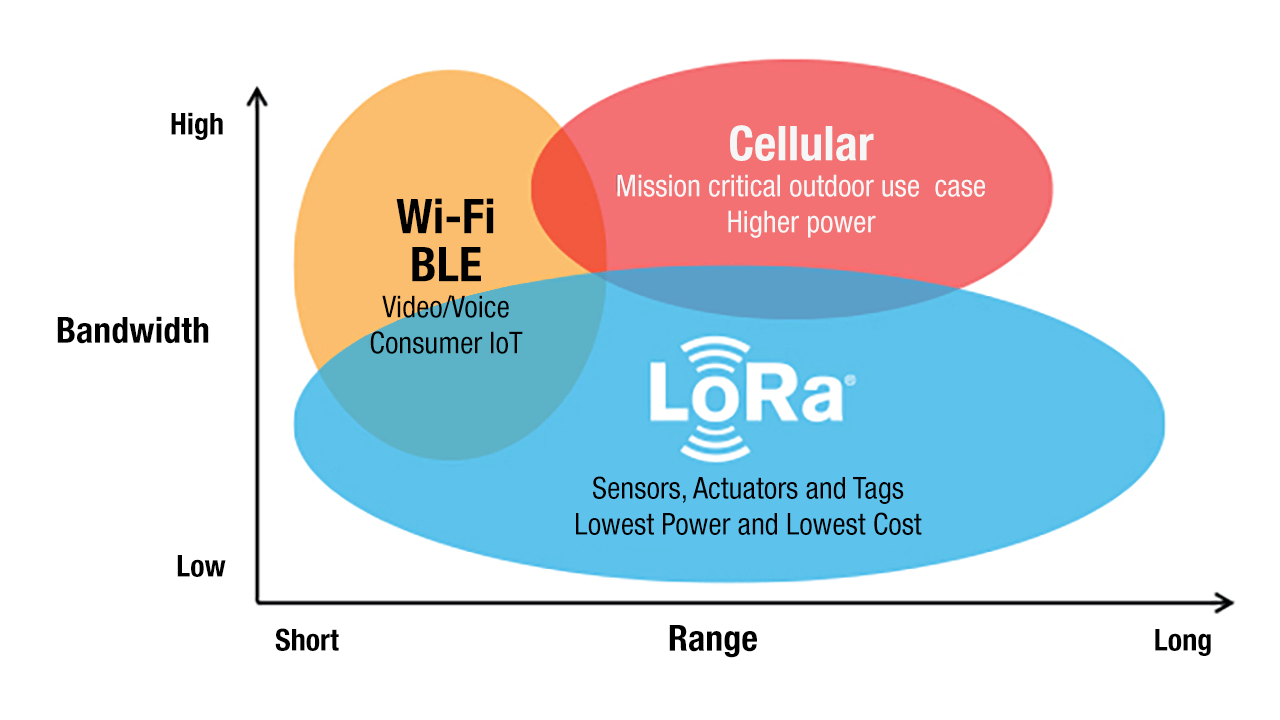
LoRa and LoRaWAN protocol
Pros: A ground-up low power wide area network (LPWAN) design that offers low battery consumption with a lifetime of up to 10 years depending on the deployment. It also spans a long range and can seamlessly be integrated to the Cloud. Furthermore, the technology secure by design and cost efficient to roll out and offers an open business model for public, private and open community use.
Cons: Not ideal of applications requiring high data rates, nor applications requiring lower latency.
Wi-Fi
Pros: Wi-Fi offers equivalent broadband performance than 5G enabling flexible rollout business models (private, public, and consumer). Wi-Fi enables cost efficient deployment processes while fostering open roaming across domestic markets and globally
Cons: Limited coverage range and requires high energy to properly operate.
BLE
Pros: BLE is low power consumption, cost-efficient, simple to setup and delivers accurate indoor location features.
Cons: The IoT technology offers low bandwidth and short range.
Zigbee
Pros: Zigbee is low power consumption, flexible for users and developers through its backward compatibility, and offers mesh capabilities.
Cons: Has a short range, high maintenance cost and complexity as well as a fragmented ecosystem, deploying not interoperable versions of Zigbee.
NB-IoT
Pros: Can leverage existing 4G coverage, handle large volumes of data and has a download capacity on licensed spectrum.
Cons: Has high battery consumption by design and mobility issues, high cost LTE roll out for massive IoT use cases only, features a complex ecosystem, and multiple releases.
LPWAN and sensors
IoT solutions like LoRa devices and the LoRaWAN protocol are driving LPWAN and sensor deployments for the IoT on land, at sea and even in space. Additionally, it not only offers connectivity for traditional IoT applications, but provides incredible benefits for critical infrastructure and solves some of the biggest challenges facing our planet across smart cities, rural areas, supply chain and logistics, and far more.
Recently, we’ve seen a reinforced need for connectivity due to the COVID-19 pandemic and how desperately the World relies on IoT technology. However, 3.7 billion people across the globe lack connectivity, especially those in more rural locations. By integrating IoT solutions like long range, low power technology, two-way communications to and from satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is enabled, and those in rural areas who would otherwise be without it, have access to affordable global connectivity. These rural areas may not have the proper broadband coverage or hardware in place to support constant connectivity, therefore 5G isn’t the appropriate choice.
Marc Pegulu, vice president of IoT product marketing and strategy, Semtech