Industry NewsMay 10, 2018
Microgrid testbed results from Industrial Internet Consortium

The Microgrid Testbed's goal to enhance the flexibility of real-time analytics and control, while increasing efficiencies, achieved 100% renewable energy via distributed energy resources in the test environment.
The Industrial Internet Consortium has announced that its microgrid testbed has achieved significant milestones, along with publishing a “Synchronized and Business-Ready Microgrid” whitepaper on its website. IIC members Real-Time Innovations (RTI), the IIoT connectivity company, and Wipro Limited, a global information technology, consulting and business process services company, authored the whitepaper based on findings from the IIC Communications & Control Testbed for Microgrid Applications (Microgrid Testbed), which also includes IIC members Cisco and National Instruments.
Microgrid Testbed
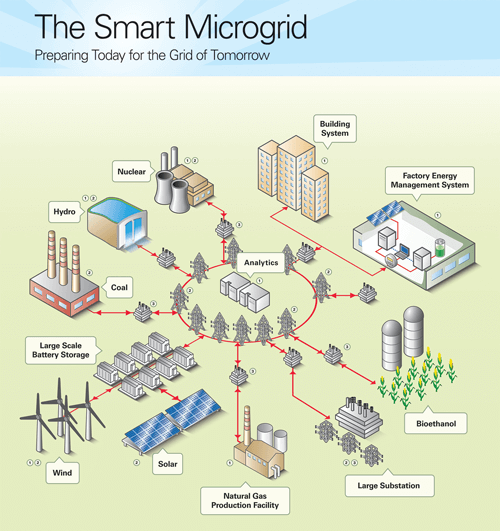 Traditional central-station power grids operate on 15-minute output update cycles that force operators to over-generate power to compensate for potential blackouts, for example, when solar arrays lose the sun, or unexpected new power demands on the grid, such as when a neighborhood plugs in several electric vehicles.
Traditional central-station power grids operate on 15-minute output update cycles that force operators to over-generate power to compensate for potential blackouts, for example, when solar arrays lose the sun, or unexpected new power demands on the grid, such as when a neighborhood plugs in several electric vehicles.
The IIC Microgrid Testbed began in 2015 with a goal to introduce the flexibility of real-time analytics and control to increase efficiencies in this legacy process, ensuring that power is generated more accurately and reliably. This whitepaper offers some of the findings from this testbed, including:
- The ability to connect an active 100% renewable energy-based microgrid back to the main power grid
- Application and device independence through the support of the Open Field Message Bus (OpenFMB) architecture standard
- Visualization, control and analytics to support efficient operations
- Integration with third party data and support of varying business models
“The emergence of generation and storage technologies, such as solar and wind, has enabled grid operators to feed power back to the main grid and reduce demand for fossil fuels. However, renewable energy sources generate direct current and require conversion to alternating current at the exact phase and frequency as the main grid,” said Brett Murphy, Senior Director, Market Development, Industrial IoT, RTI and co-author of the IIC whitepaper.
“Synchronizing these inverters as renewable generation rises above 40% of the total generation in a portion of the grid is quite challenging and can fail, leading to a blackout. Cisco, NI, RTI and Wipro created a testbed to experiment with new approaches to address the challenge. We’ve developed techniques for a 100% renewable power generation-based microgrid to support a variety of business models and demonstrated success in our test environment.”
Time-sensitive networking
The microgrid testbed uses time-sensitive networking (TSN), the latest real-time Ethernet network, between the inverter nodes to provide sub-millisecond synchronized measurement of phase, frequency and voltage. This enables the frequency, voltage and phase angle of each renewable energy source in the microgrid to be synchronized and controlled in real time, enhancing the operation of the microgrid and facilitating the enhanced penetration of distributed energy resources (DERs).
The testbed uses a standards-based approach, using the Data Distribution Service (DDS) standard from The Object Management Group to securely collect data from field devices, and the OpenFMB standard from the North American Energy Standards Board to future proof designs for grid operators.
“Microgrid solutions can help grid operators mitigate some of the issues caused by fluctuations in demand and supply curves by contextualizing collected data with external data, such as weather forecasts and real-time pricing and demand,” said Dr. Manjari Asawa, Director, IoT Partner Engineering at Wipro Limited, and co-author of the IIC whitepaper.
“The microgrid testbed includes a cloud-based platform that monitors and controls field devices in real-time or near real-time for intelligent analytics. The platform can help operators estimate power supply and work with the local balancing authority for grid stability by controlling smart loads. It can also be integrated with the utility backend system to ensure full visibility and control of the operation of the grid and to provide a dashboard for distribution and microgrid operators and in some cases, end users,” he added.
“These results show some of the benefits testbeds can bring to companies working in the IIoT ecosystem,” said Brett Burger, Principal Marketing Manager, Monitoring Solutions, NI. “The control algorithms developed combined with technologies like TSN and DDS, could help make it easier to deploy microgrids or even integrate larger scale renewable energy sources into existing grids in the near future.”
The full “Synchronized and Business-Ready Microgrid” whitepaper and a list of IIC members who contributed can be found on the IIC website:
https://www.iiconsortium.org/pdf/Synchronized_and_Business-Ready_Microgrid_20180426.pdf.


