TechnologyMarch 23, 2025
Maximizing TSN: unlocking benefits & overcoming challenges

TSN bridges the gap between today's fragmented networks and the unified networks of tomorrow by enhancing standard Ethernet with standardized, deterministic, high-performance networking capabilities that enable the seamless integration of various industrial Ethernet protocols into one unified network.
Imagine a factory floor where machines communicate with each other with such precision that even a millisecond of delay can lead to costly downtime. How can we prevent a scenario like this and ensure the timely and accurate transmission of data? What if an advanced Ethernet technology, prioritizing every millisecond, galvanized a complete shift in industrial automation?
This is the promise of time-sensitive networking (TSN), a cutting-edge technology set to revolutionize industrial automation. The numbers don’t lie: analysts project that the global TSN market will grow by a staggering 58.3% annually, reaching a value of USD 1.7 billion by 2028, according to a MarketsandMarkets report.
In this article, we will explore what is driving the rise of TSN, how it’s reshaping industrial efficiency, the challenges when deploying this technology, and ways to tackle these challenges.
Key benefits of adopting TSN
TSN’s transformative power is evident, for example, in a major home appliance manufacturer, resulting in significant improvements across several key areas:
Deterministic Communication: The low-latency, deterministic traffic scheduling of TSN allowed for precise control and synchronization of production line devices. This enhanced real-time control and overall system responsiveness, crucial for maintaining high performance in data-intensive environments.
Interoperability: TSN enabled the seamless integration of diverse production equipment from different vendors, simplifying network management and optimization. This streamlined network management and optimization ensured consistent compatibility and performance throughout the production line.
Convergence of IT and OT: By unifying IT and OT systems on a single network, TSN streamlined operations, reduced overhead, and enabled faster decision making.
Simplified Network Complexity: TSN consolidated network communications into a single, simplified architecture based on standard Ethernet, reducing complexity and costs while allowing for easy scalability.
Enhanced Productivity: TSN’s ability to prioritize control data and ensure timely transmission enhanced productivity for the manufacturer, resulting in reduced downtime, faster response times, and increased equipment effectiveness.
The cumulative effect of these enhancements was improved operational efficiency, higher productivity, and substantial progress towards the manufacturer’s goals for efficiency and precision.
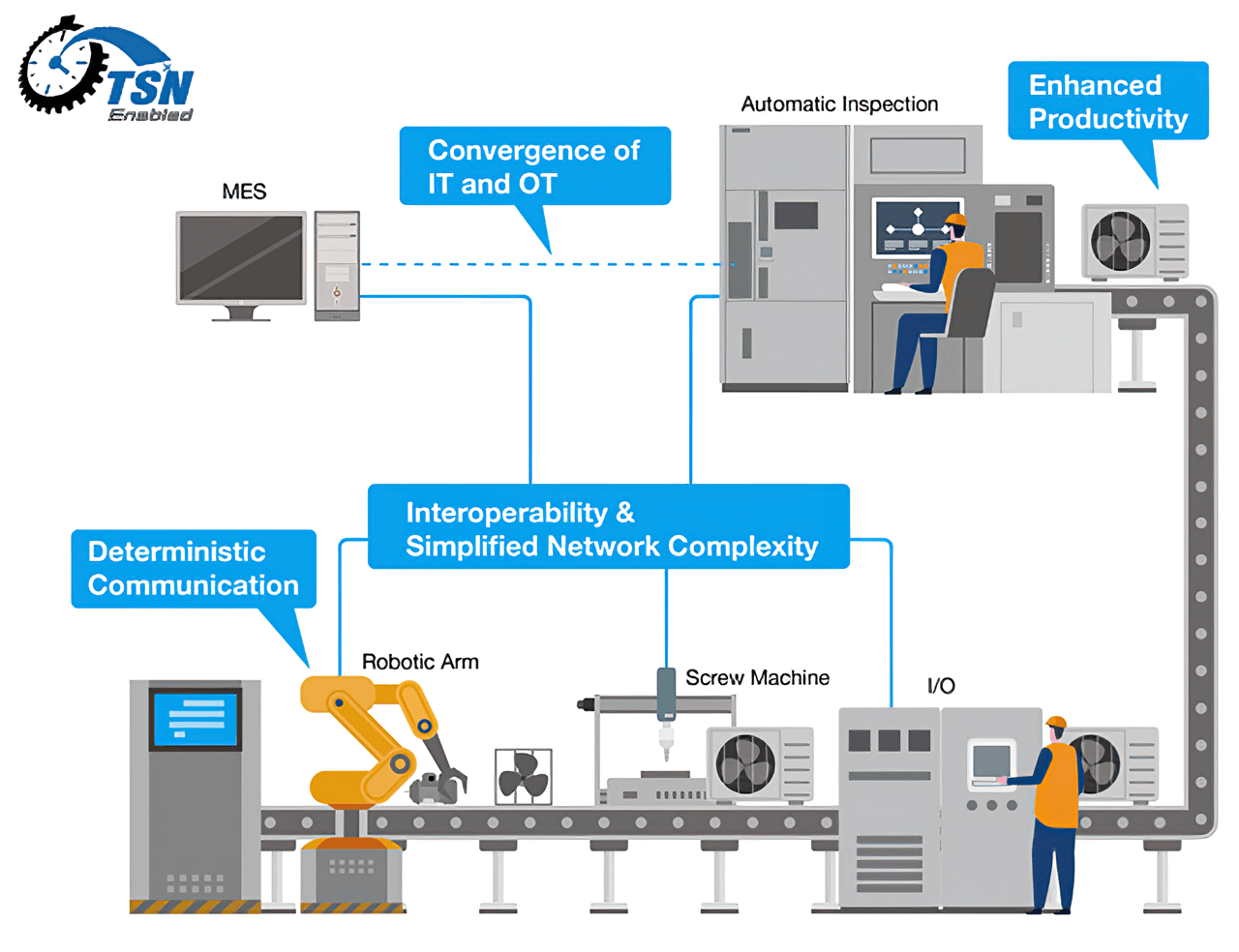
TSN provides basic productivity and communication tools for enhancing the convergence of IT and OT systems.
Possible hurdles of adopting TSN technology
TSN offers convincing benefits that make it appealing for businesses to integrate their systems and assets into a unified TSN-powered industrial network. While there are benefits to combining mission-critical and non-critical networks, integrating a new technology such as TSN will introduce additional challenges. Organizations considering implementing the new technology may have concerns regarding these requirements. The following section will focus on these specific requirements and offer strategies for successful implementation. The key challenges include:
Growing Data Volumes: As more devices and applications connect to networks, the amount of data traffic surges, requiring high-bandwidth capabilities to effectively handle this increased demand. While Gigabit and 10G connections are crucial for speed, they also come with increased costs and complexity in network resource management. The effective handling of bandwidth becomes even more critical as advanced applications like AI and machine learning continue to put a strain on these systems.
Network Management Complexity: With the growth of connected devices in a converged TSN network, managing the network will become more complex. Sophisticated management and configuration tools, such as Central Network Controllers (CNCs), are essential for simplifying these processes. However, enterprises may feel overwhelmed when implementing these solutions, given the need for technology investment, training, and ongoing maintenance.
System Compatibility: Using products that adhere to relevant testing specifications or are integrated into established testbeds makes achieving a smooth TSN implementation easier. These standards ensure compatibility and reliability, which are critical for easing integration challenges and speeding up efficiency gains. However, finding, validating, and integrating these standardized products can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, often requiring specialized expertise to navigate the various standards and certifications.
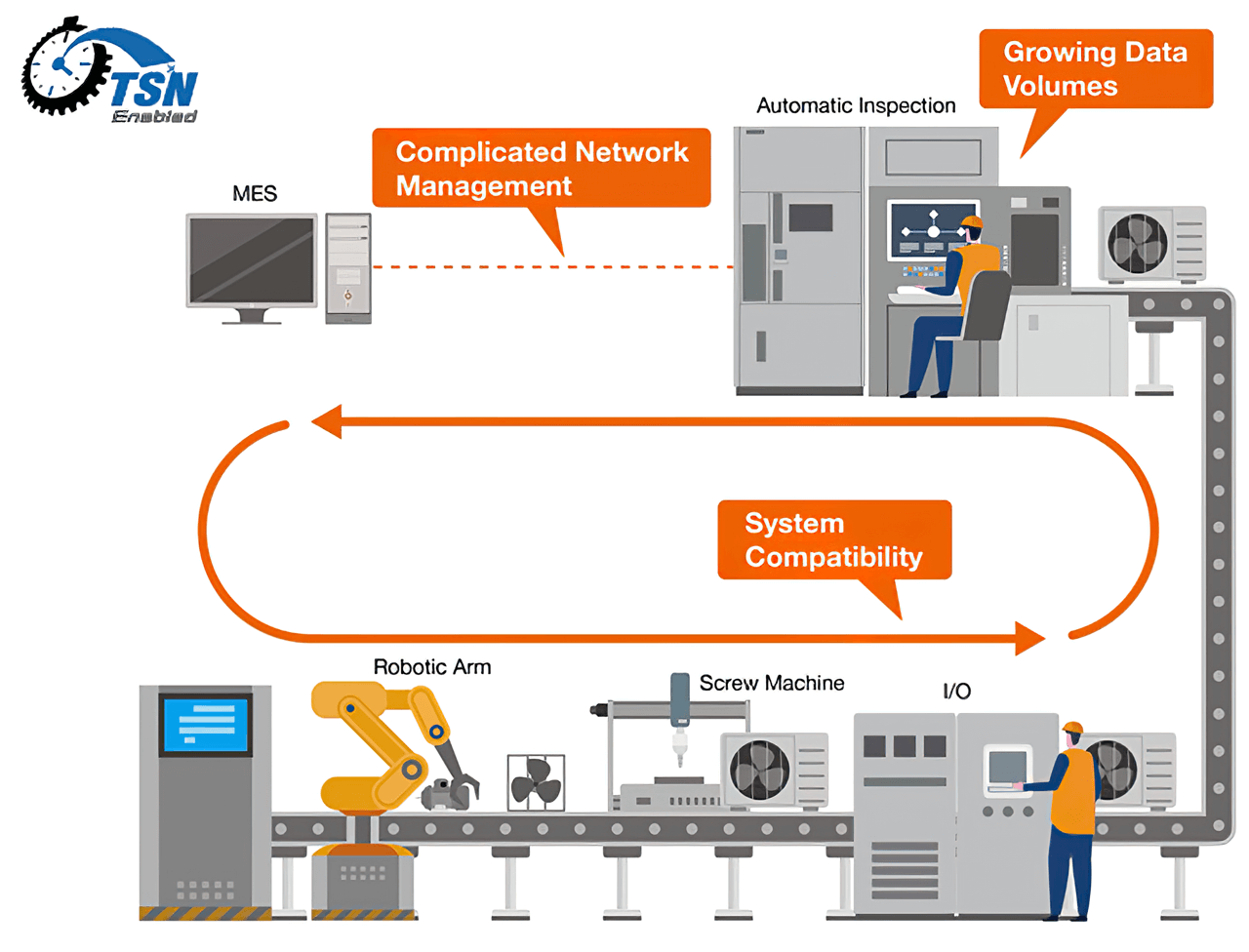
TSN solutions simplify network management, providing system compatibility and tools for analyzing vast amounts of manufacturing data.
The path to successful TSN integration
It’s important to recognize that TSN integration involves complexities. As mentioned before, the benefits—including improved real-time control, seamless interoperability, and converged network architectures—are substantial, but there are also challenges to address.
To ensure a successful deployment, organizations must consider multiple critical aspects:
Full Gigabit Performance: As data demands increase in industrial environments, efficient handling of higher data volumes necessitates high-bandwidth capabilities. Therefore, it is crucial to choose TSN solutions that support full Gigabit speeds on each port to ensure robust network performance. High-bandwidth and low-latency communication are vital for maintaining real-time data exchange, enabling precise control and responsiveness essential for complex industrial processes.
Easy Configuration: Look for intuitive management tools, such as web-based graphical user interfaces (GUIs), that simplify device setup and management. This is particularly important for large-scale deployments where complexities can escalate.
Compact and flexible design: Choose equipment with a compact and adaptable design that can easily fit into small areas. Space-saving designs allow for seamless integration of advanced networking capabilities into your existing infrastructure.
Compatibility: Make sure the products align with the required testing specifications or are included in existing testbeds. Adhering to these standards helps guarantee seamless compatibility and reliable performance, essential for successful TSN integration.


