TechnologyMarch 28, 2019
Smart cities transformed using LoRa technology
Smart city technologies provide new solutions for smarter and improved city services. A scalable and low cost IoT network is the cornerstone of a Smart City program, and LoRa-based devices and the LoRaWAN specification helps create high-capacity, low power networks that form the basis of smart city solutions.
Cities are growing and are adopting new smart solutions to better manage services, improve quality of life and reduce operating expenses in a sustainable way. LoRa technology is expected to be a critical component in the success of these initiatives.
The world’s population is increasingly moving to cities, which has kicked off a quest to use smart city technology to help cities build a sustainable infrastructure that provides smart governance, smart energy, smart mobility, smart infrastructure, smart technology, smart healthcare, and smart citizens.
Smart city technology is one way that governments and municipalities provide sustainable services required to meet this urban influx effectively. LoRa technology and low power, wide area networks (LPWAN) based on the LoRaWAN protocol provide a smart sensing and control infrastructure, which allows cities to collect and analyze data from thousands of connected devices in a streamlined manner, in order to make intelligent decisions about the services they need to offer.
LoRaWAN-based networks deliver secure, bi-directional communication with long data transmission range to blanket an urban area using minimal network infrastructure. LoRa technology delivers solutions that are optimized for smart city applications that rely on battery-powered sensors that need up to 20 years of battery life. Smart city technology is changing the way cities, governments and citizens interact, and LoRa Technology is a contributing enabler of these solutions.

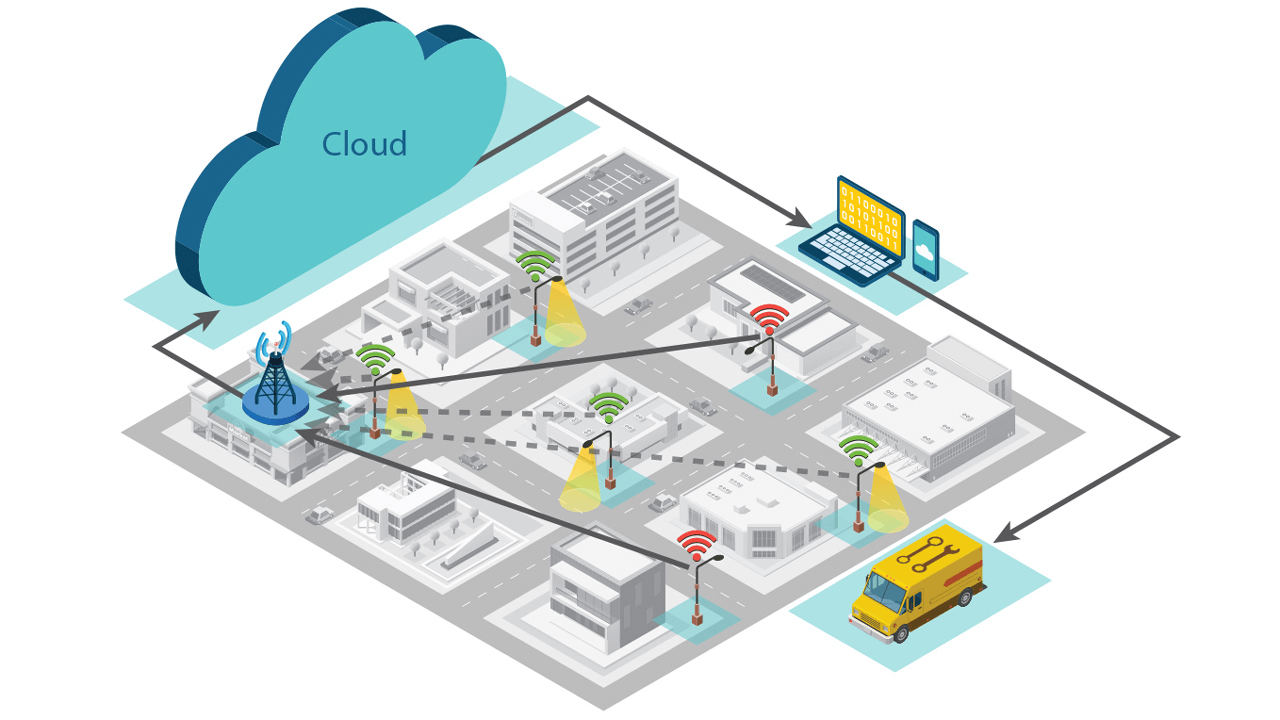
LoRa-based air pollution monitoring system.
Smart city trends and developments
Smart city initiatives are increasing as government agencies and municipalities deploy wide area networks to gather data and use advanced applications and cloud-based or enterprise-based systems to process and analyze the data. These emerging networks are called Internet of Things, or IoT networks.
These initiatives seek to place sensors and other types of instrumentation on key systems within a city to collect data about active and passive elements that are an integral part of municipal and city services. The information is often detailed and measurable to help inform for better decisions and lead to more efficient city services.
The range of smart city applications currently in consideration is vast. Both trial and deployed projects have shown measurable impact ranging from faster car parking to better emergency healthcare. Some examples of smart city solutions include:
Parking: Smart parking monitors show parking spaces available in a city to help reduce the traffic congestion created by people looking for a parking space.
Traffic Flows: Traffic congestion is a significant challenge to urban residents, and smart traffic systems can monitor vehicle and pedestrian traffic to better route automobiles and pedestrians. This is taking place now through smart traffic lights that sense traffic and coordinate light timing, but in the future, smart traffic systems may also include communication from lights to sensors in automobiles.
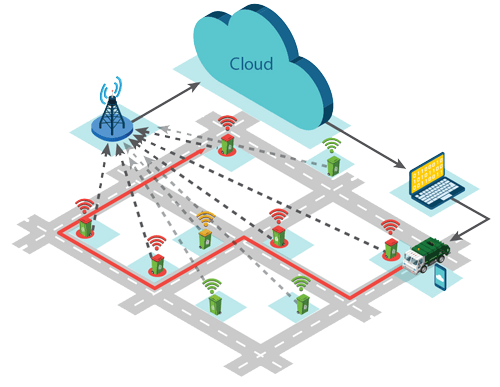
Street Lighting: Electricity from street lights is a significant municipal expense, and by better managing it, cities can save money and cut greenhouse gas emissions by reducing energy consumption. Smart street light systems provide the data cities need to reduce energy usage while maintaining well-lit streets.
Traffic Light Maintenance: Monitoring traffic lights allows municipalities to quickly respond to burned out lights, broken light poles from accidents, or malfunctioning signaling equipment. This can help with traffic congestion, potential accidents, and other hazardous situations.
Predictive Maintenance: Smart building systems can provide data that ensures structures are maintained properly by providing a predictive maintenance system. These systems can monitor vibrations and other physical conditions in buildings, bridges and historical monuments.
Waste Management: Collecting waste is an essential city service, but too often resources are used to collect under-filled waste containers when others are overflowing. Smart waste management systems can help detect garbage levels in containers to optimize the waste collection routes for efficiency and cost effectiveness. For example, alerts are triggered and pushed to maintenance specialists when a pre-determined waste level has been reached per bin, indicating waste removal is required. Levels are monitored in real-time through third-party cloud-enabled applications, optimizing maintenance response
Noise and Air Pollution: As more people move to cities, noise and air pollution become a bigger challenge. Smart noise and air pollution monitoring can provide data that can improve citizens’ well-being and detect systemic health issue correlation.
LoRa-based smart lighting system.
Measurable benefits
The goals of implementing smart city technology are to improve quality of life for the public, to create efficiency, to increase preventive response to service needs, and to more efficiently use city resources, and in turn, taxpayer dollars. With real-time data on city systems and infrastructure, officials can more easily assess the efficiency of city initiatives and make improvements as necessary.
Already, there are 14 categories of indicators for measuring the success of smart city initiatives, compiled by the International Standards Organization. These include education, health, city finances, and others, although the fast-expanding nature of smart city technology means this list is sure to grow in the coming years. Following are some real examples of how smart city projects are currently benefiting local communities:
Improving quality of life in Calgary, Alberta: The City of Calgary has deployed LoRa-based smart city solutions to better track and manage entertainment hot spots, city noise, water conservation and more. Calgary’s LoRaWAN-based network has set the stage for scalable growth and improved quality of life city-wide. These updates were made possible through the Urban Alliance, a strategic partnership between The City of Calgary and University of Calgary.
Optimizing water usage at Devonian Gardens: Calgary utilizes Semtech’s LoRa devices to monitor light, humidity, temperature and water to conserve water and park resources. By gaining an understanding of these fundamental factors, the Devonian Gardens is able to provide better care and preserve its irreplaceable plants.
Enhancing guest experience at the Shanganappi Golf Course: Location monitoring sensors provide real time information about the time it takes for customers to complete the entire course, and how long they stop at key locations. Tracking activity data allows the golf course staff to address pace of play issue elevating the customer experience and maximizing revenue.
Addressing noise pollution with the Urban Alliance: Noise pollution is a big problem for city dwellers as more people migrate to urban areas. This can impact individual health due to disturbed sleep, hearing loss, cognitive disorders and high blood pressure. Using low-cost acoustic LoRa-based sensors to enable continuous monitoring, the City of Calgary is able to more effectively handle noise management.
Game changer for smart cities
LoRa Technology offers both technical and business benefits for smart city applications. Technical benefits include the following:
Low asset deployment cost due to great indoor penetration: One gateway operates in a star network with sensors communicating directly to the gateway from a range of up to 20 kilometers. Sensors can be located indoors or outdoors. There is no need for complex coverage analysis as is required for mesh network solutions.
Low asset deployment cost due to ease of installation: Battery-operated sensors are capable of lasting up to 20 years depending on the application being used. This means there is no need for power source wiring for sensors as opposed to existing solutions such as
Secure: AES-128 encryption is built-in.
Open standard: The LoRaWAN specification is supported and maintained by the LoRa Alliance allowing seamless and easy scalability.
Geolocation: LoRa Technology utilizes a GPS-free geolocation technology that does not require additional power.
Low connection costs: LoRa Technology operates in the unlicensed ISM band, which means no or very low spectrum costs.
Benefits for businesses
A wide range of business benefits also strengthen its appeal in Smart Cities applications.
- Available today: for public and private deployments.
- Low deployment and operational costs: when compared to emerging cellular-based solutions like LTE-M and NB-IoT.
- Open network: Cities have the capability of choosing from multiple and competing network service providers, helping to drive down prices. Or cities can deploy their own local municipal network, which can host multiple applications. The cost can be minimized by leasing bandwidth to companies within the city who want to run their own applications.
- Leverage deployed assets: LoRa robust signaling can penetrate buildings for wide ranging coverage even in dense urban areas. This allows one LoRa-based gateway to potentially cover multiple buildings within a range of 2+ kilometers.
- Growing ecosystem: The fast-growing LoRa Alliance currently comprises over 400 companies that are creating solutions using the LoRaWAN specification.
The LoRa Alliance includes major industry players and many other start-ups and network operators. Combined, this ecosystem offers multiple sources of supply from communications ICs to networks to server-based application platforms. The LoRa Alliance also certifies sensors and other devices for interoperability.
Conclusion
As cities move toward efficiency, smart city technologies can provide new solutions for smarter and improved city services. A scalable and low cost IoT network is the cornerstone of a Smart City program, and LoRa-based devices and the LoRaWAN specification provide high-capacity, low power networks that form the basis of successful smart city solutions.