TechnologyJuly 16, 2024
Enabling Smart Manufacturing with Private 5G Communications

As smart manufacturing continues towards Industry 4.0, the role of private 5G networks becomes increasingly pivotal. Moxa's contributions in mitigating pain points and providing robust solutions position the company as a key player in shaping the future of connectivity in smart manufacturing.
The emerging world of smart manufacturing has been made possible by the tremendous amount of data that can be transmitted and processed today. As real-time monitoring and control increase efficiency and return on investment, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)-enabled factory floor can also embrace large-scale, cost-effective customization at short notice, delivering a competitive edge for many industries.
To build truly automated, intelligent, and robust industrial applications, communication capabilities must meet a set of stringent requirements. 5G networks, boasting unprecedented speeds, check all the boxes. With extensive capabilities, private 5G is perfect for building robust connectivity in manufacturing applications.
Not only does a private 5G network architecture offer smart manufacturing all the benefits of a 5G cellular network, such as high bandwidth, low latency, and extensive IIoT capabilities, it also features dedicated network frequencies to avoid interference from other cellular signals. As a result, private 5G networks offer improved stability and security, allowing data to be stored locally and privately, rather than on a shared public network.
This article discusses the industry trend towards adopting wireless networks in manufacturing, how smart manufacturing can benefit from private 5G, the specific pain points of implementing private 5G in the industrial context, and how the latest private 5G solutions on the market help overcome these challenges.
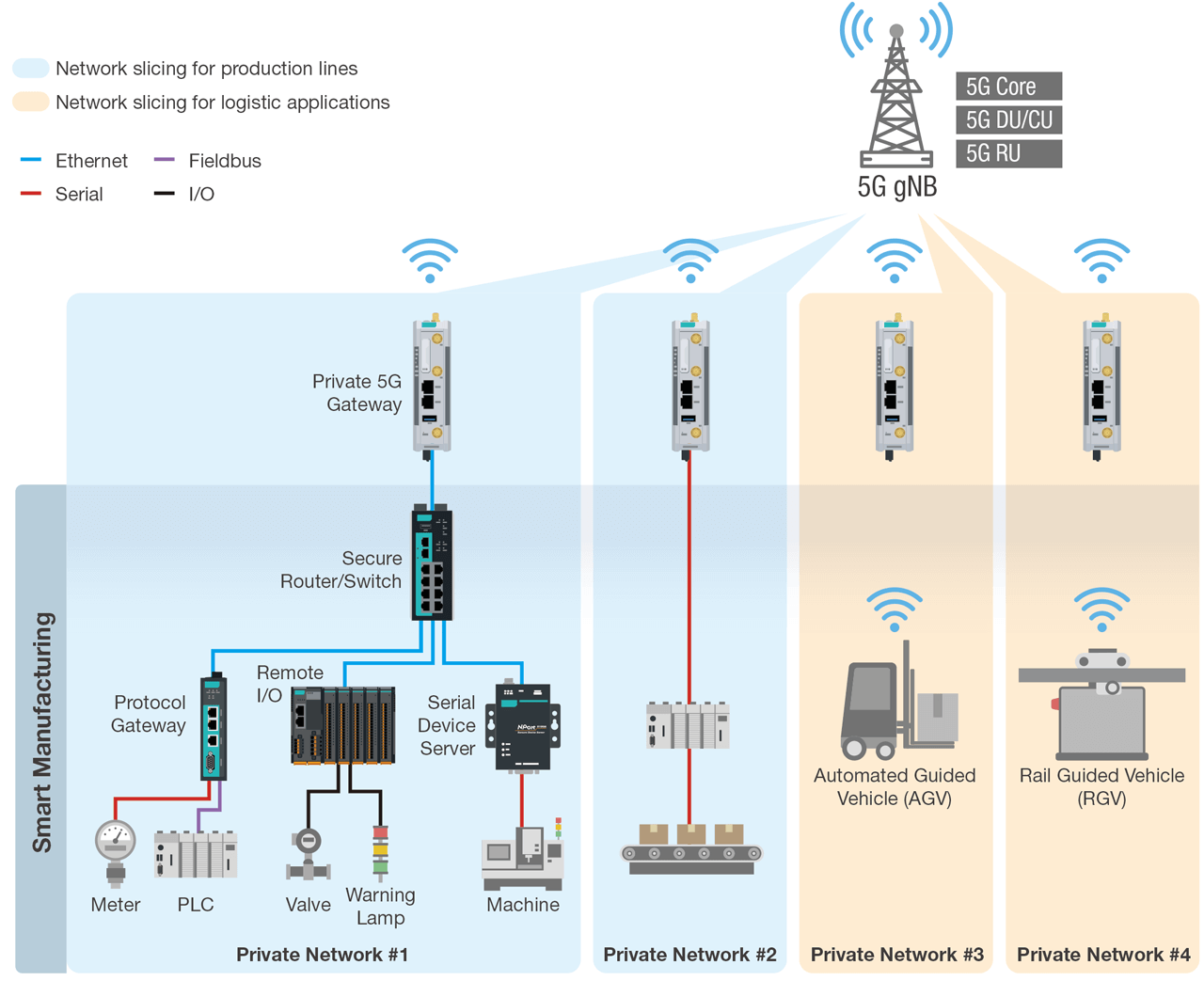
Figure 1: Private 5G networks in smart manufacturing applications.
Industry is going wireless
With the manufacturing industry moving towards Industry 4.0 and Lighthouse Factories, the amount of data transmitted using wireless technology is increasing annually and “going wireless” has become a topic of discussion in the automation industry. Therefore, in key regions promoting smart manufacturing, local governments have already designated dedicated frequencies for 5G private networks, including the United States (n48), Germany (n77), Australia (n77), Japan (n79), South Korea (n79), and Taiwan (n79). These frequencies are reserved for specific regional use and prevent wireless instability caused by interference from public network frequencies. In addition, some regions, such as China, also leverage frequencies from telecom providers for private 5G networks.
According to the Private 5G Network Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report (2023), the private 5G network market size accounts for US$2 billion and is expected to grow to US$36 billion by 2030, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 51%. These projections show a positive outlook and substantial market potential for private networks that warrants more investment.
Well-known electronic device brands and manufacturers worldwide are already developing their own 5G dedicated equipment, such as central units (CU), distributed units (DU), and radio units (RU) in the Open Radio Access Network (ORAN) framework. This trend is driven by the recognition of the extensive applications of 5G in the market and the development of its architecture. One of the primary applications is private 5G.
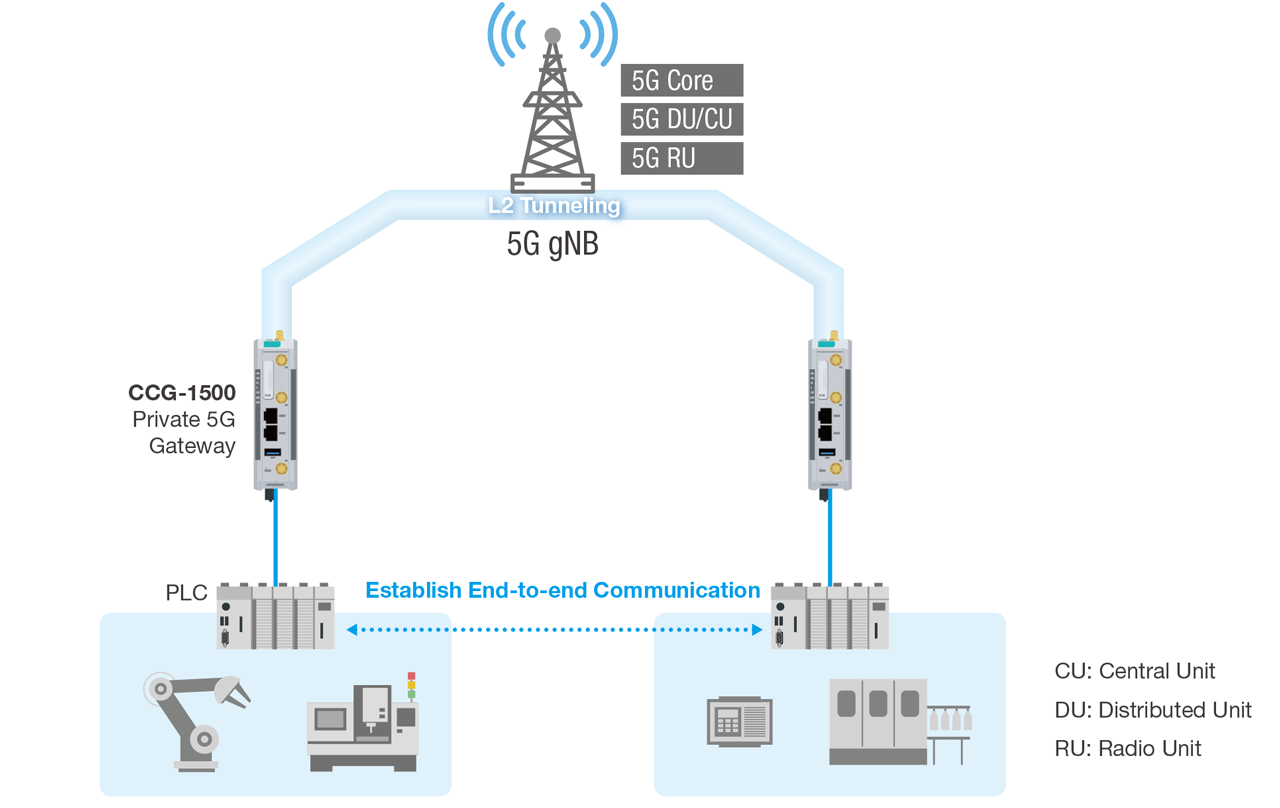
Figure 2: Layer 2 tunneling for end-to-end communication over a private 5G network.
Private 5G benefits for smart manufacturing
Smart manufacturing has unique security and stability requirements that can benefit substantially from private 5G architecture. Private 5G provides dedicated network frequencies to ensure stable signal performance without interference from other public frequencies. It also offers a customized network environment to provide the most suitable connectivity and security for specific areas. Importantly, it ensures that all data is stored locally, rather than on a public network that can be easily compromised. For example, hackers could intercept data transmitted over a public network, or infiltrate a vulnerable network and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Examples of current private 5G applications in smart manufacturing include fixed-point programmable logic controllers (PLC) as well as mobile transportation carriers, such as automated guided vehicles (AGV), automated mobile robots (AMR), and rail guided vehicles (RGV).
Industrial 5G gateways on the market often emphasize support for multiple interfaces for versatility, leading to more complex equipment architectures and bulky sizes. However, this emphasis overlooks manufacturing customers’ need for compact 5G equipment with low power consumption.
Through decades of experience in industrial automation and networking, Moxa has identified key pain points and requirements for overcoming the technical challenges of implementing private 5G networks used in smart manufacturing.

Private 5G not only enables wireless connectivity but also paves the way for a smarter, more agile, and secure industrial ecosystem. The unique benefits of private 5G, such as dedicated network frequencies, enhanced stability, and secure local data storage, align seamlessly with the specific requirements of smart manufacturing applications.
Private 5G pain points
The first major obstacle to successfully deploying a private 5G network for smart manufacturing is reconciling information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) priorities. These two domains are often at odds as IT emphasizes high security whereas OT prioritizes high availability. For example, in OT systems, production capacity and occupational safety take precedence over cybersecurity. Manufacturers cannot afford the impact of strict cybersecurity measures on production line operations, which can lead to a decrease in production capacity.
Therefore, it’s important to perform an on-site analysis to gain in-depth insights into the manufacturing processes and OT network architecture and take stock of production line assets. This requires understanding the genuine needs of customers on the OT side and translating them into a language that IT can process, with the goal of establishing an intelligent system that combines efficiency and security.
However, understanding the differences between OT and IT is only the first step. System integrators still need to overcome several challenges to implement industrial private 5G, including infrastructure deployment, device and endpoint management, and integration with existing systems.
- Infrastructure deployment: To use private 5G, integrators will need to construct the necessary infrastructure, including 5G gateways, base stations, 5G core networks, and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC). These devices are costly and have a high technical threshold that requires experienced professionals to deploy. Because all 5G deployments are unique, each site requires a customized configuration that cannot be easily copied to other sites.
- Device and endpoint management: Managing various devices and endpoints within a private 5G network is complex. This often involves using customized software to manage all 5G devices, handling tasks such as authentication, firmware updates, status monitoring, and viewing historical messages.
- Integration with existing systems: Communication protocols used by industrial equipment predominantly operate at the Layer 2 level, whereas 5G architecture works in Layer 3 and above with IP functionality. Therefore, IT professionals face the challenge of enabling 5G communication to support Layer 2 packet pass-through.
Moxa solutions
Whether building a 5G network for smart industry or implementing other OT/IT convergence projects, system operators are looking for the most efficient way to overcome pain points while lowering deployment costs.
When integrating diverse OT devices, factory engineers can leverage Moxa’s vast portfolio of serial communication products to connect a wide range of field devices. For many years, Moxa has specialized in establishing industrial communications for OT equipment, such as terminal PLCs, meters, and sensors using a wide range of protocol gateways, remote I/Os, and serial converters. Fully embracing the new 5G era, Moxa is now helping simplify the integration and transmission of data communications from these OT devices to 5G cellular networks through Moxa’s private 5G gateways.
Compact and energy-efficient
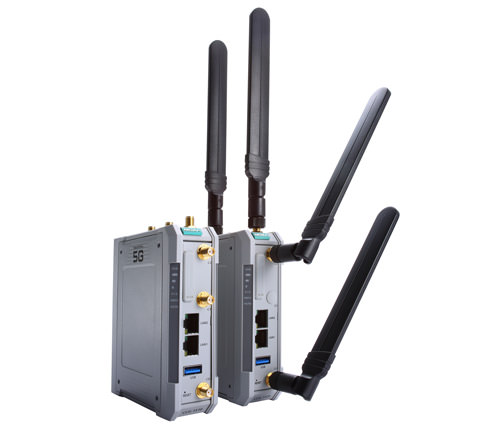

Moxa’s CCG-1500 Series
private 5G cellular gateways pack powerful performance in a compact form factor, measuring only 100 x 125 x 35 mm. Featuring customizable network settings and built-in redundancy with automatic SIM card switching, the CCG-1500 Series delivers outstanding field performance and stable network connectivity.
Moreover, the CCG-1500 Series’ low power consumption (average 8 W) allows for better battery life and fewer power inputs, reducing maintenance and operating costs over the product’s lifetime. These features are especially important for remote deployments where power efficiency is key.
IIoT compatibility and performance
Designed as both a media and a protocol converter, the CCG-1500 Series is ideal for IIoT applications. Its 5G-to-Ethernet and 5G-to-serial conversion capabilities support both public and private networks and streamline OT (Ethernet and serial) to private 5G data transmissions. Dual-SIM redundancy offers industrial-grade reliability for uninterrupted connectivity. Wide temperature models are available for extended temperature applications. All CCG-1500 Series models are thoroughly tested in a testing chamber to ensure reliable 5G performance in wide-temperature environments.
Ethernet frame tunneling with Layer 2 data packets
Moxa’s private 5G solutions enable Ethernet frame tunneling services, making it possible for Layer 2 data packets to be transmitted over the 5G network as end-to-end (E2E) communication between two or more terminal devices. Seamless E2E communication allows data packets from the central control to reach end devices securely over a private 5G network, saving time and resources otherwise spent managing devices on-site.
Accessories to boost performance
Prior to the official launch of the CCG-1500 Series, Moxa conducted proof-of-concept (PoC) verifications with several major customers and found that many factories often ignore the potential signal interference caused by operational equipment or metal partitions when deploying their private 5G infrastructure. This oversight can result in poor signal quality and attenuation, as well as additional costs by having to deploy more radio units (RUs) to maintain signal quality.
Moxa offers additional accessories to optimize the performance of the CCG-1500 Series private 5G gateways. The LNA-1000 Series low-noise amplifiers (LNA) strengthen reception quality and support 5G cellular bands. Meanwhile, the BST-1000 Series signal boosters enhance signal output power and support the n48 and n78 bands.
Moxa’s BST-1000 Series is the first signal amplifier on the market to support TDD Duplex mode. The BST-1000 Series can enhance the signal strength and signal transmission distance of CCG-1500 Series 5G gateways by up to 50%. In environments with heavy signal interference, the BST-1000 Series helps enhance the signal to ensure a stable connection to the cellular base station.
Network oversight and management software
A private 5G network needs to be constantly monitored and maintained for optimal performance. Moxa’s Device Lifecycle Management (DLM) software allows trained IT and OT operators to perform device management. With support for the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) LwM2M protocol, DLM makes it easy for administrators to have a centralized view of the network and identify potential issues quickly. With DLM, users can perform secure software updates, monitor the network status, access logs, troubleshoot, and perform other network management functions all in one place.
Summary
As smart manufacturing continues towards Industry 4.0, the role of private 5G networks becomes increasingly pivotal. Moxa’s contributions in mitigating pain points and providing robust solutions position the company as a key player in shaping the future of connectivity in smart manufacturing.
Private 5G not only enables wireless connectivity but also paves the way for a smarter, more agile, and secure industrial ecosystem. The unique benefits of private 5G, such as dedicated network frequencies, enhanced stability, and secure local data storage, align seamlessly with the specific requirements of smart manufacturing applications.
Moxa, with its comprehensive suite of products and decades of expertise, addresses the 5G migration challenges by offering compact and energy-efficient solutions like the CCG-1500 Series private 5G gateway.
The inclusion of features such as Ethernet frame tunneling for end-to-end communication, signal booster and low-noise amplifier accessories, and network oversight and management software show Moxa’s commitment to providing reliable and tailored 5G solutions for the industrial sector.
Jun CH Wang, Product Manager Industrial Wireless Division, Moxa Inc.