TechnologyJuly 14, 2021
Transforming industries and challenges with Edge-AI
Analog compute-in-memory takes advantage of high-density flash memory to enable compact, single chip processor designs. It dramatically reduces power consumption and, by reducing the barriers of cost, size, power and performance, companies can truly rethink what’s possible with AI.
Today companies have only scratched the surface of what AI is capable of at the edge. The full potential of AI is being constrained by a number of different factors. One challenge has been the limited compute capabilities of edge devices, at least until recently.
Additionally, edge inference, what enables a neural network to perform different functions when encountering real-world data, has been a major technical challenge. The good news is that advancements in edge-AI processing are working to solve these challenges and open up a new world of AI-powered possibilities.
Let’s take a look at the top five industries that will be transformed by edge-AI.
Different Segments for Industrial Automation
Industrial Automation
Over the past few decades, factories have become more and more automated, bringing efficiency to new heights and driving down the costs of the goods that consumers use every day. While factories have already deployed computer vision (CV) to optimize production lines, factories can now take advantage of new edge-AI processing technologies to combine the power of CV with AI, especially deep learning (DL).
This will significantly improve factory throughput and quality, two essential metrics for an efficient production line. As factories become more automated with interactive human-to-machine processes, AI is also being used to deliver a new level of workplace safety. Just imagine a food processing factory with AI-powered collaborative robots to inspect cereal boxes on the production line in real time.
Deploying AI solutions for industrial automation is a challenge. Automation engineers in the manufacturing field don’t have the expertise to develop effective AI/DL algorithms. However, several AI technology companies are removing these hurdles by providing a complete inference solution – high performance and low-power hardware in a small form factor, along with ready-to-deploy DL algorithms. We’ll see more investment being poured into this area as more factories want to take advantage of powerful edge-AI processing to improve efficiency and workplace safety.
Aerospace/Drones
Edge-AI processing is also enabling many different types of physical surveillance applications for drones. Drones are being outfitted with ultra-high definition cameras that can be used for many CV applications, including monitoring agricultural yields, inspecting critical infrastructure such as power lines, cell phone towers, bridges and wind farms, inspecting fire damage, examining coastline erosion, and much more. These tasks often require running complex AI networks locally to provide immediate and relevant information to the control station, so it’s important to have powerful AI processors that are also extremely power-efficient.
Smart Home
AI voice applications have already reshaped the home as we know it, bringing intelligence to all sorts of devices from speakers to TVs and refrigerators. The next smart home revolution will be powered by vision applications. One of the most interesting AI capabilities is human pose estimation – when a camera sensor can detect and track movement of your body parts – which can be used for a wide variety of applications.
Take AR/VR gaming, for example, where AI could track gamers’ movements from head to toe and then instantly render those movements as their character on the screen for a truly immersive gaming experience. AR/VR requires instantly processing information from cameras and LiDAR, time-of-flight (ToF), and audio sensors, so edge-AI processing is a must.
Smart fitness is another exciting use case. There are already some popular fitness applications that use pose estimation to monitor users’ movements and then provide corrections and recommendations. Instead of going to the gym, consumers can learn from an AI trainer right in their living room.
We’ll also see AI-enabled robots become increasingly popular in the smart home. The idea of smart home robots was popularized in the Jetsons TV series with the robot maid Rosie which could talk, clean and take care of other household tasks. That vision for a truly smart robot is getting closer to reality. In the coming years we’ll see robotic vacuums that see and avoid obstacles with AI to clean faster and more efficiently, unlike the ones of the past that would wander around the home aimlessly. Autonomous lawn mowers are another type of CV robot that will become mainstream in the years ahead.
Data Centers
When you think of data centers you might not think about edge-AI computing. However, edge-AI processing can enable data centers to run neural networks at scale across all of their data streams. Companies can use AI processors to support a broad range of neural networks, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and dense networks.
This makes it possible to process high resolution data accurately across neural networks to perform inference across live data. Since neural network inference is compute-intensive and power-hungry, traditionally it has required costly hardware, advanced cooling infrastructure, and kilowatts of power. New technologies have made it possible for processors to be extremely powerful and power-efficient, while also being scalable so they can easily fit into companies’ existing infrastructure.
Physical Security
Having security cameras can make a big difference in catching criminals and keeping people safe. However, there has been a lot of debate about cameras providing safety monitoring.
AI seems to be adding to this anxiety, even though it can actually be used to better protect people’s privacy – if AI is applied appropriately. In current systems, cameras capture images of people and objects and send that information to a command center for visual analysis; this is where the uneasiness comes with being monitored constantly. A better alternative is to have cameras that use trained AI algorithms to detect specific sequences – accidents, crimes, or other events – and only send the footage of potential security incidents for analysis.
This approach delivers the safety and security the public desires while providing the privacy all of us expect. Cameras today are already equipped with computer vision techniques. To reach the next level of safety and privacy, high performance edge-AI capabilities in the camera will be required for traffic monitoring, incident detection, facial recognition, and many more applications to come in the future.
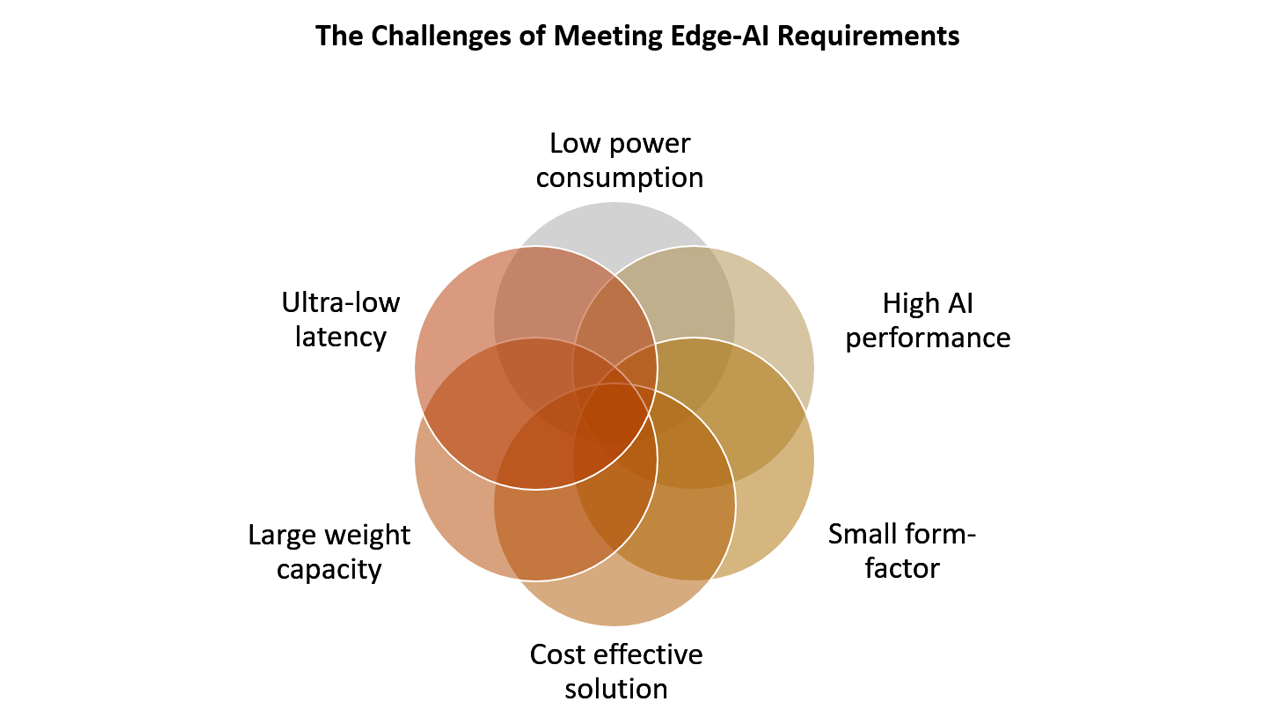
AI processing at the edge requires silicon that can meet demanding requirements for size, performance, and power consumption. A new approach – analog compute in flash memory – promises to solve these challenges and make it possible to widely deploy powerful edge-AI. Digital AI processors are extremely expensive to deploy and are very complex to develop, which has restricted innovation to the biggest technology companies.
Analog compute-in-memory takes advantage of high-density flash memory to enable compact, single chip processor designs. Perhaps even more importantly, analog compute-in-memory dramatically reduces power consumption, making it 10X more efficient than digital systems while still enabling extremely high performance computing. By reducing the barriers of cost, size, power, and performance, companies can truly rethink what’s possible with AI.