TechnologyMarch 23, 2025
Power of TSN and RTOS integration for aerospace
The integration of TSN and RTOS is not just a technological advancement; it is a strategic enabler for the next generation of networked systems. By providing a unified, deterministic and high-bandwidth communication solution, TSN and RTOS together pave the way for groundbreaking innovations in avionics, space and defense.
Integration of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) with Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) marks a transformative milestone for the Aerospace industry.
This article examines TSN’s ability to deliver deterministic, reliable, and high-bandwidth communication, addressing aerospace’s unique demands through the IEEE P802.1DP profile. By unifying protocols and optimizing architectures, TSN enhances performance, reduces complexity, and ensures Safety-critical communication. Its applications in Avionics, Space, and Defence systems streamline networks, cut costs, and support mixed-criticality traffic.
Together, TSN and RTOS enable future-ready, efficient, and resilient systems, redefining connectivity and laying the groundwork for innovation in Aerospace and beyond.
TSN: strategic enabler for avionics and space industries
Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) is not merely an enhancement to Ethernet; it is a transformative approach that redefines the capabilities of networked systems in critical sectors. The Avionics and Space industries, where precision and reliability are not luxuries but necessities, find in TSN a technology that aligns with their visionary pursuits.
The advent of TSN marks a significant milestone in the evolution of network technologies. Its introduction into the Avionics and Space industries heralds a new era of connectivity, where the potential for innovation is matched by the performance of the network.
Unified technology: the convergence of capabilities
TSN stands out as a unified solution that encapsulates the core requirements of modern avionics systems. It converges reliability, determinism, and high bandwidth into a singular, robust framework, paving the way for a new generation of networked systems.
The Ethernet backbone of TSN offers unparalleled market benefits. It taps into an established ecosystem, bringing with it the advantages of a wide array of COTS products, a large market presence, and a diverse pool of vendors. This positions TSN as a technology not just of the present but also of the future.
Reliability: the foundation of trustworthy communication
At the heart of TSN lies the promise of reliability, a promise that is critical in unforgiving critical environments.
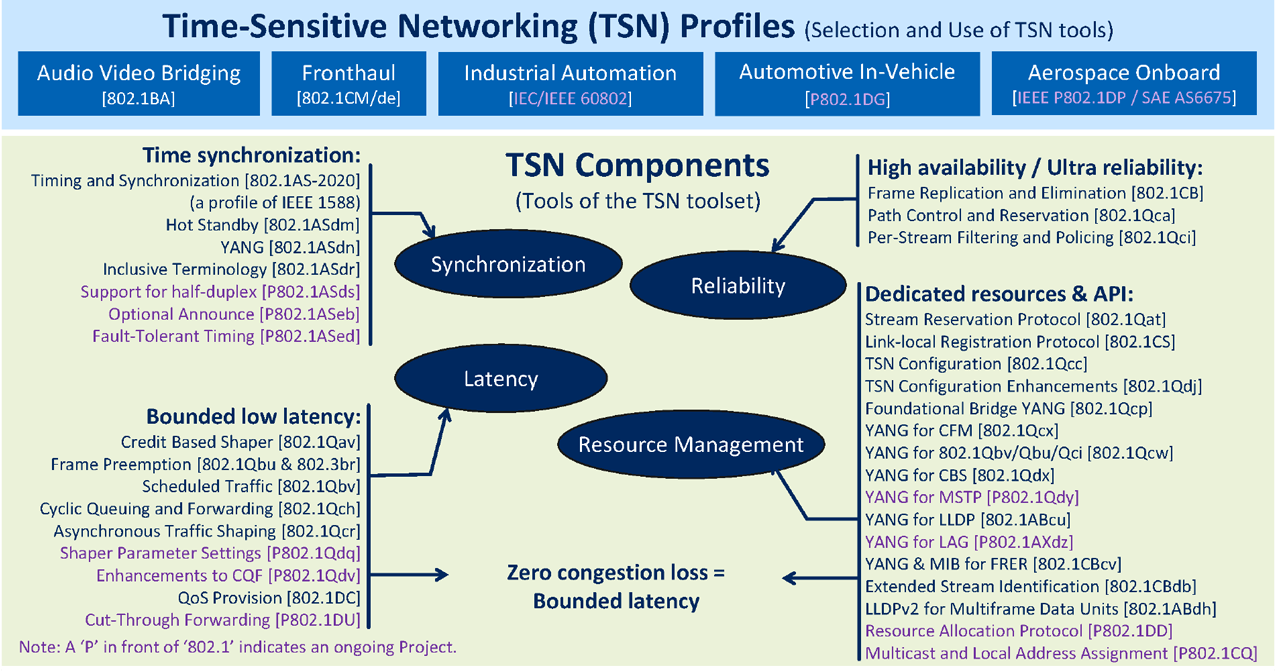
The IEEE 802.1CB standard introduces mechanisms like FRER (Frame Replication and Elimination for Reliability), which ensure continuous communication even in the face of potential network disruptions. Complementing this, IEEE 802.1Qci provides stringent filtering and policing, fortifying the network against errors and enhancing its resilience.
Synchronization: Orchestrating a Unified Network Tempo Synchronization is the conductor of the network orchestra, ensuring each device plays in harmony with the others.
With IEEE 802.1AS at its core, TSN achieves a level of synchronization that is imperative for the coordinated tasks of the missions. This standard is the linchpin for operations where every nanosecond counts.
Latency: the pursuit of immediate responsiveness
In the realm of real-time operations, latency is the difference between success and failure.
TSN addresses low and bounded latency through a suite of protocols, each designed to ensure that time-critical data is accorded the highest priority and delivered within the tightest timeframes, thus maintaining the rhythm of real-time responsiveness. IEEE 802.1Qbv (Time Aware Shaper) and 802.1Qav (Credit Based Shaper), and 802.1Qbu for Frame Preemption ensures the QoS and constrains for the critical flows.
Resource management: maximizing network efficiency
Effective resource management is akin to a well-orchestrated ballet, where each movement is both precise and purposeful.
The IEEE 802.1Qcc standard is the choreographer of network resources, directing traffic with an eye for efficiency and an understanding of the network’s dynamic needs.
IEEE P802.1DP aerospace profile
The aerospace profile of TSN, IEEE P802.1DP, is a testament to the adaptability of TSN to the specialized needs of the aerospace sector.
Recognizing the diverse nature of aerospace applications, the IEEE P802.1DP profile accommodates both synchronous and asynchronous communication needs. This dual modality ensures that TSN can support a wide range of applications and legacy implementations, from those requiring strict timing to those that can tolerate some degree of latency.
The profile outlines the supported TSN protocols, each selected for its ability to transport time-sensitive data streams with the precision and reliability that Aerospace applications demand. It is a profile that not only meets the current needs of the industry but also anticipates its future directions.
This expanded introduction provides a holistic view of TSN’s role in avionics and space industries, setting the stage for a detailed exploration of its integration with RTOS and the synergies that arise from this powerful combination.
The importance of Real-Time Operating Systems with TSN
Operating Systems (OS) are pivotal in managing the allocation of processing elements, such as processors or cores, to various software units, known as threads or processes. This allocation occurs both physically and temporally. In Symmetrical Multiprocessor Systems (SMP), an OS determines which processor a specific thread or process runs on and when it gets to use the processing element, balancing its usage with other processes.
General Purpose Operating Systems
General-purpose operating systems often prioritize performance, immediately allocating available processing elements to pending software units.
While this approach can be efficient, it may lead to issues such as cache contention. Modern processors contain first-level caches that store memory blocks for executing applications. Arbitrary allocation can degrade cache performance, causing variability in application execution times. Affinity policies can mitigate this effect.
Another example is operating systems that prioritize responsiveness, attending to interruptions promptly. While this enhances user experience, it can disrupt executing applications, preventing consistent execution times.
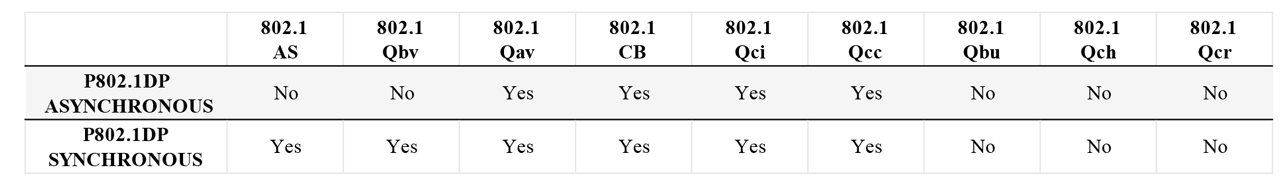
Table 1. TSN Protocols required as defined on IEEE P802.1DP for Aerospace TSN Profile
Real-Time Operating Systems
In contrast, Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) emphasize determinism, allowing system architecture to make predefined decisions rather than the OS itself. Features like reduced context switching and increased responsiveness (e.g., PREEMPT_RT in Linux) are beneficial but insufficient alone for deterministic execution in critical safety systems.
RTOS, such as PikeOS, enable physical partitioning of the system and resource allocation to specific software units. These units are restricted to their allocated resources, preventing interference with other partitions. Temporal partitioning is also crucial, ensuring software units do not exceed their allocated execution time. This is particularly challenging in multicore systems, where shared resources like internal buses can cause interference. RTOS can help minimize such interferences, essential for certifying high Safety-critical systems on multicore architectures.
This concept, known as Robust Resource and Time Partitioning, is outlined in the avionics standard ARINC 653. The system’s timeline is defined, and software units are allocated accordingly, ensuring controlled resource usage.
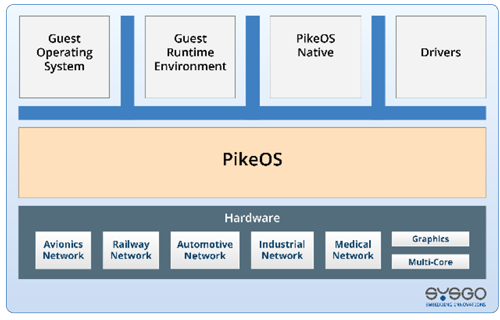
Figure 2. PikeOS RTOS architecture
RTOS with TSN
System time is typically maintained by an external crystal, driving various system clocks. In RTOS, this clock source ensures time coherence between software units. However, synchronization with external systems can be challenging. Precision Time Protocol (PTP, IEEE 1588) addresses this by defining a master-slave architecture for clock distribution, using timestamped messages to synchronize clocks across the network. TSN adopts a subset of PTP (IEEE 802.1AS) for sub-microsecond precision and supports wireless communications.
With time synchronization established, TSN can implement additional functionalities like scheduling, traffic shaping, and stream reservation protocols. TSN ensures synchronized clock sources, enabling harmonious and deterministic behavior across the entire technical ecosystem. This synchronization is often essential for the proper functioning of broader critical Safety-related systems.
Applicability of TSN in aerospace
The following case studies illustrate the diverse applications of TSN technology across the aerospace industry, highlighting its role in enhancing the performance, reliability, and efficiency of embedded real-time systems.
Case Study 1: TSN for Spacecraft Avionics
The space industry traditionally relies on various communication protocols such as MIL-STD-1553, SpaceWire, AFDX, and TTEthernet to meet mission requirements. These protocols cater to different network needs in terms of determinism, reliability, and high bandwidth, resulting in complex multi-protocol networks within spacecraft. TSN, with its deterministic and high-bandwidth capabilities, offers a unified Ethernet-based solution that can replace these multi-protocol networks, simplifying the architecture, reducing costs, and enhancing performance.
TSN’s features also make it highly useful in Next Generation Launcher Communication Systems. Leading Space agencies, such as ESA and NASA, have recognized their importance and have shown significant interest in R&D projects aimed at developing such technologies and innovations.
OSRA-NET (Open System Architecture for Real-time Applications) is a framework that defines traffic classes to prioritize different types of data in real-time systems. In satellite and launcher communication, OSRA-NET traffic classes can be mapped onto TSN Quality of Service (QoS) classes to ensure efficient data transmission. For example, critical telemetry and control data can be mapped to high-priority TSN classes, ensuring minimal latency and jitter. Medium-priority classes can handle mission data that requires timely delivery but can tolerate some delays, while low-priority classes can be used for non-critical data such as housekeeping information.
A practical example of TSN in the space industry is the use of GNSS-based synchronization. The Global Navigation Satellite System provides accurate timing information, which can be utilized for synchronization in TSN networks through the IEEE 802.1AS standard. GNSS receivers on spacecraft and launchers provide precise timestamps, which are distributed across the TSN network. These timestamps synchronize all network devices, ensuring that data is transmitted and received at the correct times. This synchronization is vital for maintaining the determinism and reliability of data in Space applications, enabling seamless and efficient communication.
Once the network is synchronized, an Attitude and Orbit Control System (AOCS) control loop can be integrated within TSN’s 802.1Qbv (Time-Aware Shaper) windows. By scheduling AOCS control loop data within Qbv windows, the system ensures that critical control commands are transmitted with minimal delay, improving the performance of AOCS actuators. This integration enhances the stability and control of both satellites and launchers, demonstrating the benefits of TSN in mission-critical applications.
In addition to improving performance and reliability, TSN contributes to significant weight reduction in launchers by simplifying the network architecture and reducing the need for extensive wiring. This weight reduction translates into cost savings, as the cost of putting an additional kilogram of payload into orbit remains significant despite recent reductions with reusable stage launchers.
In summary, TSN offers significant advantages for the space industry by providing a unified, deterministic, and high-bandwidth communication solution. TSN can enhance the performance and reliability of both satellite and launcher avionics systems, paving the way for more advanced and efficient space missions.
Case Study 2: TSN for Aircraft Avionics
In avionics control units, managing mixed-criticality traffic while ensuring deterministic and reliable communication is a critical issue. Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is being adopted as an upgrade over traditional ARINC 664 communication protocols, particularly in next-generation aircraft and helicopters.
Avionics systems must handle various types of data traffic with different levels of priority, ranging from non-critical data (like in-flight entertainment) to safety-critical functions (such as flight control and sensor data). TSN is highly suited for this task due to its ability to ensure deterministic communication, meaning that each packet of data reaches its destination at a guaranteed time, regardless of network load. This is essential for maintaining the precision and safety of flight control systems.
Certain control systems rely on time-sensitive algorithms, such as autopilot and collision avoidance. TSN enhances these systems by scheduling time-defined slots for critical data, ensuring that high-priority communications are always delivered on time. This mechanism is particularly important for managing communication between subsystems like sensors, actuators, and flight control units, where even minor delays can affect performance.
As avionics become more sophisticated, the number of connected devices and the amount of data they generate increases. TSN helps manage this growing complexity by efficiently handling higher traffic and subscriber counts. This reduces the need for intricate and heavy wiring harnesses, which have been a characteristic of traditional ARINC-664 P7 systems. By lowering the wiring complexity, TSN contributes to weight reduction in aircraft, improving fuel efficiency and reducing network device costs.
In summary, TSN offers a robust solution for managing mixed-critical traffic in aircraft avionics systems. By ensuring deterministic and reliable communication, TSN enhances the precision and safety of flight control systems. Its ability to handle increasing data traffic and reduce wiring complexity translates into significant weight and cost savings, making it an essential technology for next-generation aircraft and helicopters. TSN’s integration into avionics systems not only improves performance but also paves the way for more advanced and efficient aviation technologies.
Case Study 3: TSN in Defence Critical Systems
Ensuring real-time, reliable communication for mission-critical systems in resource-constrained, dynamic defence environments is a significant challenge. The NATO Generic Vehicle Architecture (NGVA) platform requires robust, low-latency communication systems to manage both high-priority video traffic and critical vehicle functions. Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) plays a crucial role by providing guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS), low-latency, and deterministic traffic management, which are essential for defence operations.
For land Defence scenarios, real-time video streaming is crucial for surveillance, target identification, and situational awareness. TSN ensures uninterrupted, high-quality video by reserving bandwidth for latency-controlled video streams, even in resource-constrained and high-demand environments.
Additionally, TSN supports seamless integration of various subsystems within military vehicles, such as navigation, communication, and weapon systems. By providing a unified network infrastructure, TSN reduces the complexity and weight of wiring harnesses, which is particularly beneficial in armored vehicles where space and weight are at a premium. This integration not only improves the overall efficiency and reliability of the vehicle’s systems but also simplifies maintenance and upgrades.
TSN’s scalability is another significant advantage for defence applications. As military technology evolves, TSN networks can easily accommodate new devices and functionalities without requiring extensive infrastructure changes. This flexibility makes TSN an ideal solution for future-proofing communication systems, ensuring they can adapt to emerging threats and technological advancements.
In summary, TSN offers substantial benefits for the Defence industry by providing a robust, low-latency, and deterministic communication solution. Its ability to handle mixed-criticality traffic, ensure real-time data transmission, and support scalable network architectures makes it an invaluable asset for modern defence operations. TSN’s integration enhances operational efficiency, reliability, and adaptability, making it a critical component in the advancement of defence technologies.
Uniting SOC-E’s TSN and PikeOS
In the realm of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN), SOC-E stands as a global leader, offering a comprehensive portfolio of solutions that range from high-performance TSN switches and endpoints to industrial-grade plug-and-play devices. SOC-E’s expertise in TSN is complemented by SYSGO’s robust PikeOS, a real-time operating system (RTOS) known for its determinism, safety, and security. This section delves into the partnership between SOC-E and SYSGO, exploring how their combined expertise in TSN and RTOS creates a powerful synergy that benefits customers across various sectors.
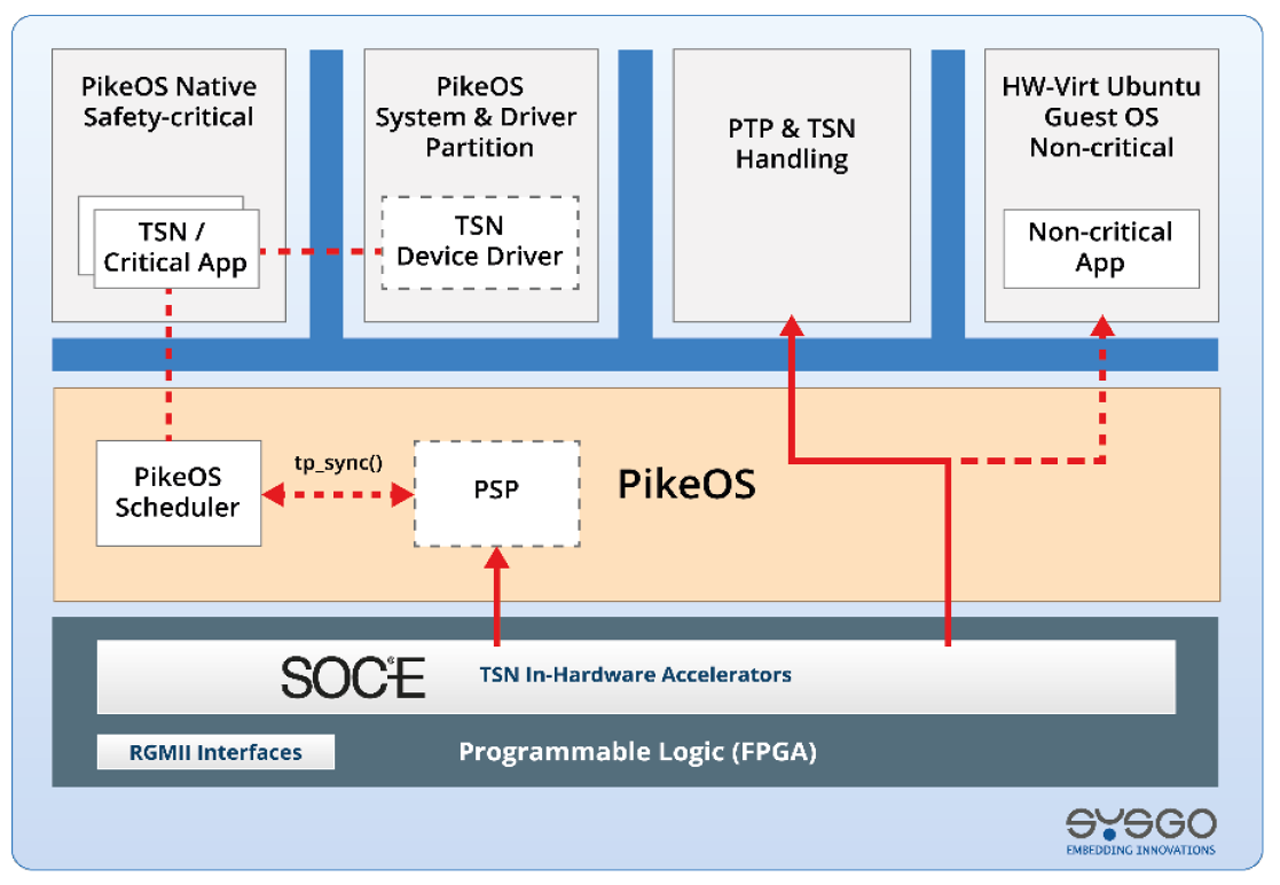
Figure 3. SOC-E’s TSN integration with PikeOS scheduler.
A strategic alliance
The collaboration between SOC-E and SYSGO represents a strategic alliance that leverages the strengths of both companies. SOC-E’s TSN solutions ensure high-bandwidth, deterministic data transfer, which is essential for the Avionics, Automotive, and Industrial Automation sectors. When combined with PikeOS, these capabilities are enhanced, resulting in:
Deterministic Performance: PikeOS’s capabilities guarantee timely delivery of critical data, augmenting the deterministic nature of SOC-E’s TSN.
Cost Efficiency: The consolidation of multiple functions onto a single platform using PikeOS’s hypervisor technology reduces hardware requirements and costs.
Certification Confidence: PikeOS’s certification kits and modular architecture streamline the certification process, providing assurance in the system’s safety and security.
Long-Term Support: SOC-E’s and SYSGO’s commitment to product life cycle support ensures that customers receive consistent and reliable software updates and support.
Next-generation systems
The synergy between SOC-E’s TSN solutions and SYSGO’s PikeOS is more than the sum of its parts. It is a perfect match that accelerates the development and deployment of next-generation systems. This partnership not only enhances the performance and reliability of TSN systems but also opens new possibilities for innovation in connected industries.
Together, SOC-E and SYSGO are driving the future of connectivity, delivering solutions that are at the forefront of technology and tailored to meet the evolving needs of the avionics and space industries.
Conclusion and outlook
The integration of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) with Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) represents a transformative leap in the Aerospace industry. This whitepaper has explored the multifaceted advantages and applications of TSN, highlighting its critical role in ensuring deterministic, reliable, and high-bandwidth communication across various high-stakes environments. The TSN Aerospace Profile IEEE P802.1DP, specifically tailored for the unique demands of aerospace applications, ensures that both synchronous and asynchronous communication needs are met with precision and reliability.
TSN is not just an enhancement to existing network protocols; it is a revolutionary approach that redefines the capabilities of networked systems. In the Avionics and Space industries, where precision and reliability are paramount, TSN offers a unified solution that integrates reliability, determinism, and high bandwidth into a robust framework. This technology is pivotal in replacing complex multi-protocol networks, simplifying architectures, reducing costs, and enhancing overall performance. The IEEE P802.1DP profile plays a crucial role in this transformation, providing a standardized approach to meet the stringent requirements of aerospace communications.
The combination of SOC-E’s TSN solutions with the robust PikeOS RTOS ensures unparalleled performance and reliability. This integration guarantees that critical data is delivered on time, reduces hardware requirements through hypervisor technology, and streamlines the certification process, providing a comprehensive solution for modern networked systems.

SOC-E solutions.
The practical applications of TSN in aerospace and defence scenarios underscore its versatility and effectiveness. In spacecraft avionics systems, TSN simplifies network architecture, improves the performance of critical control systems and reduces the overall OBDH subsystem weight, and therefore, cost. In aircraft avionics, TSN manages mixed-criticality traffic, ensuring the precision and safety of flight control systems while reducing wiring complexity and improving fuel efficiency. In defence critical systems, TSN provides robust, low-latency communication essential for mission-critical operations, supporting seamless integration of subsystems and future-proofing defence communication networks.
As we look to the future, the potential of TSN combined with RTOS is boundless. This synergy is set to drive significant advancements in connectivity, enabling more sophisticated, efficient, and reliable systems across various sectors. The ongoing commitment to innovation and long-term support ensures that solutions will continue to meet the needs of the industry.
In conclusion, the integration of TSN and RTOS is not just a technological advancement; it is a strategic enabler for the next generation of networked systems. By providing a unified, deterministic, and high-bandwidth communication solution, TSN and RTOS together pave the way for groundbreaking innovations in Avionics, Space, and Defence. This article has laid the foundation for understanding the profound impact of these technologies, setting the stage for a future where connectivity and reliability are seamlessly intertwined.